Salmonella enterotoxin (Stn) regulates membrane composition and integrity
- PMID: 22301710
- PMCID: PMC3380714
- DOI: 10.1242/dmm.009324
Salmonella enterotoxin (Stn) regulates membrane composition and integrity
Abstract
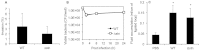
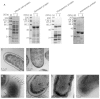
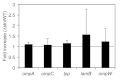
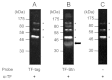
The mechanism of action of Salmonella enterotoxin (Stn) as a virulence factor in disease is controversial. Studies of Stn have indicated both positive and negative effects on Salmonella virulence. In this study, we attempted to evaluate Stn function and its effects on Salmonella virulence. To investigate Stn function, we first performed in vitro and in vivo analysis using mammalian cells and a murine ileal loop model. In these systems, we did not observe differences in virulence phenotypes between wild-type Salmonella and an stn gene-deleted mutant. We next characterized the phenotypes and molecular properties of the mutant strain under various in vitro conditions. The proteomic profiles of the total cell membrane protein fraction differed between wild type and mutant in that there was an absence of a protein in the mutant strain, which was identified as OmpA. By far-western blotting, OmpA was found to interact directly with Stn. To verify this result, the morphology of Salmonella was examined by transmission electron microscopy, with OmpA localization being analyzed by immunogold labeling. Compared with wild-type Salmonella, the mutant strain had a different pole structure and a thin periplasmic space; OmpA was not seen in the mutant. These results indicate that Stn, via regulation of OmpA membrane localization, functions in the maintenance of membrane composition and integrity.
Figures

References
-
- Abdallah B. M., Boissy P., Tan Q., Dahlgaard J., Traustadottir G. A., Kupisiewicz K., Laborda J., Delaisse J. M., Kassem M. (2007). dlk1/FA1 regulates the function of human bone marrow mesenchymal stem cells by modulating gene expression of pro-inflammatory cytokines and immune response-related factors. J. Biol. Chem. 282, 7339–7351 - PubMed
-
- Chai T. J., Foulds J. (1997). Purification of protein A, an outer membrane component missing in Escherichia coli K-12 ompA mutants. Biochim. Biophys. Acta 493, 210–215 - PubMed
-
- Chopra A. K., Peterson J. W., Chart P., Prasad R. (1994). Molecular characterization of an enterotoxin from Salmonella typhimurium. Microb. Pathog. 16, 85–98 - PubMed
-
- Chopra A. K., Huang J. H., Xu X. J., Burden K., Niesel D. W., Rosenbaum M. W., Popov V. L., Peterson J. W. (1999). Role of Salmonella enterotoxin in overall virulence of the organism. Microb. Pathog. 27, 155–171 - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

