Exhaustive swimming differentially inhibits P2X1 receptor- and α1-adrenoceptor-mediated vasoconstriction in isolated rat arteries
- PMID: 22301861
- PMCID: PMC4010332
- DOI: 10.1038/aps.2011.148
Exhaustive swimming differentially inhibits P2X1 receptor- and α1-adrenoceptor-mediated vasoconstriction in isolated rat arteries
Abstract
Aim: To investigate the effects of exhaustive swimming exercise on P2X1 receptor- and α1-adrenoceptor-mediated vasoconstriction of different types of arteries in rats.
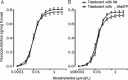
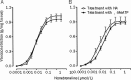
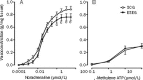
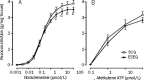
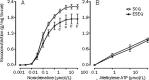
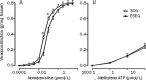
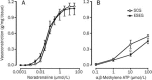
Methods: Male Wistar rats were divided into 2 groups: the sedentary control group (SCG) and the exhaustive swimming exercise group (ESEG). The rats in the ESEG were subjected to a swim to exhaustion once a day for 2 weeks. Internal carotid, caudal, pulmonary, mesenteric arteries and aorta were dissected out. Isometric vasoconstrictive responses of the arteries to α,β-methylene ATP (α,β-MeATP) or noradrenaline (NA) were recorded using a polygraph.
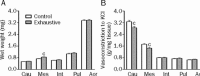
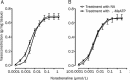
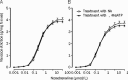
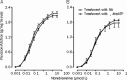
Results: The exhaustive swimming exercise did not produce significant change in the EC(50) values of α,β-MeATP or NA in vasoconstrictive response of most of the arteries studied. The exhaustive swimming exercise inhibited the vasoconstrictive responses to P2X1 receptor activation in the internal carotid artery, whereas it reduced the maximal vasoconstrictive responses to α1-adrenoceptor stimulation in the caudal, pulmonary, mesenteric arteries and aorta. The rank order of the reduction of the maximal vasoconstriction was as follows: mesenteric, pulmonary, caudal, aorta.
Conclusion: Exhaustive swimming exercise differentially affects the P2X1 receptor- and α1-adrenoceptor-regulated vasoconstriction in internal carotid artery and peripheral arteries. The ability to preserve purinergic vasoconstriction in the peripheral arteries would be useful to help in maintenance of the basal vascular tone during exhaustive swimming exercise.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Neuropeptide Y facilitates P2X1 receptor-dependent vasoconstriction via Y1 receptor activation in small mesenteric arteries during sympathetic neurogenic responses.Vascul Pharmacol. 2021 Feb;136:106810. doi: 10.1016/j.vph.2020.106810. Epub 2020 Nov 9. Vascul Pharmacol. 2021. PMID: 33181321
-
Raised tone reveals purinergic-mediated responses to sympathetic nerve stimulation in the rat perfused mesenteric vascular bed.Eur J Pharmacol. 2007 Jun 1;563(1-3):180-6. doi: 10.1016/j.ejphar.2007.02.011. Epub 2007 Feb 17. Eur J Pharmacol. 2007. PMID: 17367778
-
[Effect of isosorbide-5-mononitrate on sympathetic purinergic vasoconstriction of the rabbit saphenous artery].Yao Xue Xue Bao. 2007 Aug;42(8):833-7. Yao Xue Xue Bao. 2007. PMID: 17944230 Chinese.
-
Congestive heart failure induces downregulation of P2X1-receptors in resistance arteries.Cardiovasc Res. 1999 Jul;43(1):219-27. doi: 10.1016/s0008-6363(99)00060-7. Cardiovasc Res. 1999. PMID: 10536707
-
Physiological significance of P2X receptor-mediated vasoconstriction in five different types of arteries in rats.Purinergic Signal. 2011 Jun;7(2):221-9. doi: 10.1007/s11302-011-9226-y. Epub 2011 May 11. Purinergic Signal. 2011. PMID: 21559787 Free PMC article.
Cited by
-
(-)Doxazosin is a necessary component for the hypotensive effect of (±)doxazosin during long-term administration in conscious rats.Acta Pharmacol Sin. 2014 Jan;35(1):48-57. doi: 10.1038/aps.2013.154. Epub 2013 Dec 16. Acta Pharmacol Sin. 2014. PMID: 24335843 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Kingwell BA. Nitric oxide-mediated metabolic regulation during exercise: effects of training in health and cardiovascular disease. FASEB J. 2000;14:1685–96. - PubMed
-
- Sutoo D, Akiyama K. Regulation of brain function by exercise. Neurobiol Dis. 2003;13:1–14. - PubMed
-
- Larson EB, Wang L. Exercise, aging, and Alzheimer disease. Alzheimer Dis Assoc Disord. 2004;18:54–6. - PubMed
-
- Sastre J, Asensi M, Gasco E, Pallardo FV, Ferrero JA, Furukawa T, et al. Exhaustive physical exercise causes oxidation of glutathione status in blood: prevention by antioxidant administration. Am J Physiol. 1992;263:R992–5. - PubMed
-
- Banerjee AK, Mandal A, Chanda D, Chakraborti S. Oxidant, antioxidant and physical exercise. Mol Cell Biochem. 2003;253:307–12. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

