A novel sulfonamide agent, MPSP-001, exhibits potent activity against human cancer cells in vitro through disruption of microtubule
- PMID: 22301862
- PMCID: PMC4010333
- DOI: 10.1038/aps.2011.156
A novel sulfonamide agent, MPSP-001, exhibits potent activity against human cancer cells in vitro through disruption of microtubule
Abstract
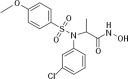
Aim: To evaluate the anti-cancer effects of a new sulfonamide derivative, 2-(N-(3-chlorophenyl)-4-methoxyphenylsulfonamido)-N-hydroxypropanamide (MPSP-001).
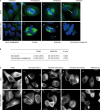
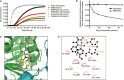
Methods: Human cancer cell lines (HepG2, THP-1, K562, HGC-27, SKOV3, PANC-1, SW480, Kba, HeLa, A549, MDA-MB-453, and MCF-7) were examined. The cytotoxicity of MPSP-001 was evaluated using the WST-8 assay. Cell cycle distribution was examined with flow cytometry. Mitotic spindle formation was detected using immunofluorescence microscopy. Apoptosis-related proteins were examined with Western blot using specific phosphorylated protein antibodies. Competitive tubulin-binding assay was performed to test whether the compound competitively bound to the colchicine site. Molecular docking was performed to explore the possible binding conformation.
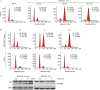
Results: MPSP-001 potently inhibited the growth of the 12 different types of human cancer cells with the IC(50) values ranging from 1.9 to 15.7 μmol/L. The compound exerted potent inhibition on the drug-resistant Kb/VCR and MCF-7/ADR cells, as on Kba and MCF-7 cells. In HeLa, HGC-27, A549, and other cells, the compound (5 μmol/L) caused cell cycle arrest at the G(2)/M phase, and subsequently induced cell apoptosis. In Hela cells, it prevented the mitotic spindle formation. Furthermore, the compound dose-dependently inhibited polymerization of tubulin in vitro, and directly bound to the colchicine-site of β-tubulin. Molecular docking predicted that the compound may form two hydrogen bonds to the binding pocket. The compound showed synergistic effects with colchicine and taxol in blocking mitosis of HeLa cells.
Conclusion: MPSP-001 shows a broad-spectrum of anti-tumor efficacy in vitro and represents a novel structure with anti-microtubule activity.
Figures

References
-
- Urruticoechea A, Alemany R, Balart J, Villanueva A, Vinals F, Capella G. Recent advances in cancer therapy: an overview. Curr Pharm Des. 2010;16:310. - PubMed
-
- Gan PP, McCarroll JA, Po'uha ST, Kamath K, Jordan MA, Kavallaris M. Microtubule dynamics, mitotic arrest, and apoptosis: drug-induced differential effects of betaIII-tubulin. Mol Cancer Ther. 2010;9:1339–48. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

