Control of cytokine mRNA expression by RNA-binding proteins and microRNAs
- PMID: 22302144
- PMCID: PMC3383846
- DOI: 10.1177/0022034512437372
Control of cytokine mRNA expression by RNA-binding proteins and microRNAs
Abstract
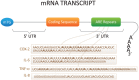
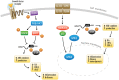
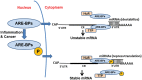
Cytokines are critical mediators of inflammation and host defenses. Regulation of cytokines can occur at various stages of gene expression, including transcription, mRNA export, and post- transcriptional and translational levels. Among these modes of regulation, post-transcriptional regulation has been shown to play a vital role in controlling the expression of cytokines by modulating mRNA stability. The stability of cytokine mRNAs, including TNFα, IL-6, and IL-8, has been reported to be altered by the presence of AU-rich elements (AREs) located in the 3'-untranslated regions (3'UTRs) of the mRNAs. Numerous RNA-binding proteins and microRNAs bind to these 3'UTRs to regulate the stability and/or translation of the mRNAs. Thus, this paper describes the cooperative function between RNA-binding proteins and miRNAs and how they regulate AU-rich elements containing cytokine mRNA stability/degradation and translation. These mRNA control mechanisms can potentially influence inflammation as it relates to oral biology, including periodontal diseases and oral pharyngeal cancer progression.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that there are no conflicts relevant to this manuscript.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Inflammation: cytokines and RNA-based regulation.Wiley Interdiscip Rev RNA. 2010 Jul-Aug;1(1):60-80. doi: 10.1002/wrna.1. Epub 2010 May 6. Wiley Interdiscip Rev RNA. 2010. PMID: 21956907 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Systematic analysis of cis-elements in unstable mRNAs demonstrates that CUGBP1 is a key regulator of mRNA decay in muscle cells.PLoS One. 2010 Jun 21;5(6):e11201. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0011201. PLoS One. 2010. PMID: 20574513 Free PMC article.
-
[Aberrant regulation of mRNA 3' untranslated region in cancers and inflammation].Med Sci (Paris). 2008 Mar;24(3):290-6. doi: 10.1051/medsci/2008243290. Med Sci (Paris). 2008. PMID: 18334178 Review. French.
-
Cellular mutants define a common mRNA degradation pathway targeting cytokine AU-rich elements.RNA. 2001 Nov;7(11):1578-88. RNA. 2001. PMID: 11720287 Free PMC article.
-
Evaluating posttranscriptional regulation of cytokine genes.Methods Mol Biol. 2012;820:71-89. doi: 10.1007/978-1-61779-439-1_5. Methods Mol Biol. 2012. PMID: 22131026 Free PMC article.
Cited by
-
The Assembly of EDC4 and Dcp1a into Processing Bodies Is Critical for the Translational Regulation of IL-6.PLoS One. 2015 May 13;10(5):e0123223. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0123223. eCollection 2015. PLoS One. 2015. PMID: 25970328 Free PMC article.
-
Circ_0015756 Aggravates Hepatocellular Carcinoma Development by Regulating FGFR1 via Sponging miR-610.Cancer Manag Res. 2020 Aug 18;12:7383-7394. doi: 10.2147/CMAR.S262231. eCollection 2020. Cancer Manag Res. 2020. PMID: 32884351 Free PMC article.
-
The ARE-binding protein Tristetraprolin (TTP) is a novel target and mediator of calcineurin tumor suppressing function in the skin.PLoS Genet. 2018 May 3;14(5):e1007366. doi: 10.1371/journal.pgen.1007366. eCollection 2018 May. PLoS Genet. 2018. PMID: 29723192 Free PMC article.
-
MicroRNAs and periodontal disease: a qualitative systematic review of human studies.J Periodontal Implant Sci. 2021 Dec;51(6):386-397. doi: 10.5051/jpis.2007540377. J Periodontal Implant Sci. 2021. PMID: 34965618 Free PMC article.
-
A C-terminal peptide from type I interferon protects the retina in a mouse model of autoimmune uveitis.PLoS One. 2020 Feb 26;15(2):e0227524. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0227524. eCollection 2020. PLoS One. 2020. PMID: 32101556 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Anderson P. (2009). Intrinsic mRNA stability helps compose the inflammatory symphony. Nat Immunol 10:233-234 - PubMed
-
- Audic Y, Hartley RS. (2004). Post-transcriptional regulation in cancer. Biol Cell 96:479-498 - PubMed
-
- Bhattacharyya SN, Habermacher R, Martine U, Closs EI, Filipowicz W. (2006). Relief of microRNA-mediated translational repression in human cells subjected to stress. Cell 125:1111-1124 - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
- R00DE018191/DE/NIDCR NIH HHS/United States
- R01 DE018290/DE/NIDCR NIH HHS/United States
- F32 DE021305/DE/NIDCR NIH HHS/United States
- R01DE018512/DE/NIDCR NIH HHS/United States
- R00 DE018191/DE/NIDCR NIH HHS/United States
- 1R01DE018290/DE/NIDCR NIH HHS/United States
- 5F32DE021305/DE/NIDCR NIH HHS/United States
- R00DE018165/DE/NIDCR NIH HHS/United States
- R01 DE021423/DE/NIDCR NIH HHS/United States
- 2P20 RR017696/RR/NCRR NIH HHS/United States
- P20 RR017696/RR/NCRR NIH HHS/United States
- R21DE017977/DE/NIDCR NIH HHS/United States
- R01 DE018512/DE/NIDCR NIH HHS/United States
- R00 DE018165/DE/NIDCR NIH HHS/United States
- R21 DE017977/DE/NIDCR NIH HHS/United States
- 1R01DE021423/DE/NIDCR NIH HHS/United States
- K02DE0219513/DE/NIDCR NIH HHS/United States
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

