Quantitative analysis of perfusion studies: strengths and pitfalls
- PMID: 22302181
- PMCID: PMC3412547
- DOI: 10.1007/s12350-011-9509-2
Quantitative analysis of perfusion studies: strengths and pitfalls
Abstract
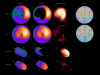
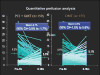
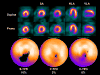
Tools for automated quantification of myocardial perfusion are available to nuclear cardiology practitioners and researchers. These methods have demonstrated superior reproducibility with comparable diagnostic and prognostic performance, when compared with segmental visual scoring by expert observers. A particularly useful application of the quantitative analysis can be in the detection of subtle changes or in precise determination of ischemia. Some challenges remain in the routine application of perfusion quantification. Multiple quantitative parameters may need to be reconciled by the expert reader for the final diagnosis. Computer analysis may be sensitive to imaging artifacts, resulting in false positive scans. Perfusion quantification may require site specific normal limits and some degree of manual interaction. New software improvements have been proposed to address some of these challenges.
Figures

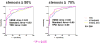

References
-
- Germano G, Kavanagh PB, Su HT, et al. Automatic reorientation of three-dimensional, transaxial myocardial perfusion SPECT images. J Nucl Med. 1995;36(6):1107–1114. - PubMed
-
- Faber TL, Cooke CD, Folks RD, et al. Left ventricular function and perfusion from gated SPECT perfusion images: an integrated method. J Nucl Med. 1999;40(4):650–659. - PubMed
-
- Slomka PJ, Nishina H, Berman DS, et al. Automated Quantification Of Myocardial Perfusion SPECT Using Simplified Normal Limits. J Nucl Cardiol. 2005;12(1):66–77. - PubMed
-
- Van Train KF, Areeda J, Garcia EV, et al. Quantitative same-day rest-stress technetium-99m-sestamibi SPECT: definition and validation of stress normal limits and criteria for abnormality. J Nucl Med. 1993;34(9):1494–1502. - PubMed
-
- Tilkemeier PL, Cooke CD, Ficaro EP, Glover DK, Hansen CL, McCallister BD., Jr American Society of Nuclear Cardiology information statement: Standardized reporting matrix for radionuclide myocardial perfusion imaging. J Nucl Cardiol. 2006;13(6):e157–171. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

