Contrast-enhanced magnetic resonance microangiography reveals remodeling of the cerebral microvasculature in transgenic ArcAβ mice
- PMID: 22302811
- PMCID: PMC6703349
- DOI: 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.5626-11.2012
Contrast-enhanced magnetic resonance microangiography reveals remodeling of the cerebral microvasculature in transgenic ArcAβ mice
Abstract
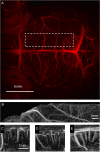
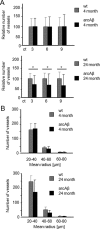
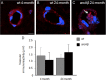
Amyloid-β (Aβ) deposition in the cerebral vasculature is accompanied by remodeling which has a profound influence on vascular integrity and function. In the current study we have quantitatively assessed the age-dependent changes of the cortical vasculature in the arcAβ model of cerebral amyloidosis. To estimate the density of the cortical microvasculature in vivo, we used contrast-enhanced magnetic resonance microangiography (CE-μMRA). Three-dimensional gradient echo datasets with 60 μm isotropic resolution were acquired in 4- and 24-month-old arcAβ mice and compared with wild-type (wt) control mice of the same age before and after administration of superparamagnetic iron oxide nanoparticles. After segmentation of the cortical vasculature from difference images, an automated algorithm was applied for assessing the number and size distribution of intracortical vessels. With CE-μMRA, cerebral arteries and veins with a diameter of less than the nominal pixel resolution (60 μm) can be visualized. A significant age-dependent reduction in the number of functional intracortical microvessels (radii of 20-80 μm) has been observed in 24-month-old arcAβ mice compared with age-matched wt mice, whereas there was no difference between transgenic and wt mice of 4 months of age. Immunohistochemistry demonstrated strong fibrinogen and Aβ deposition in small- and medium-sized vessels, but not in large cerebral arteries, of 24-month-old arcAβ mice. The reduced density of transcortical vessels may thus be attributed to impaired perfusion and vascular occlusion caused by deposition of Aβ and fibrin. The study demonstrated that remodeling of the cerebrovasculature can be monitored noninvasively with CE-μMRA in mice.
Figures



References
-
- Baltes C, Radzwill N, Bosshard S, Marek D, Rudin M. Micro MRI of the mouse brain using a novel 400 MHz cryogenic quadrature RF probe. NMR Biomed. 2009;22:834–842. - PubMed
-
- Bolan PJ, Yacoub E, Garwood M, Ugurbil K, Harel N. In vivo micro-MRI of intracortical neurovasculature. Neuroimage. 2006;32:62–69. - PubMed
-
- Bouras C, Kövari E, Herrmann FR, Rivara CB, Bailey TL, von Gunten A, Hof PR, Giannakopoulos P. Stereologic analysis of microvascular morphology in the elderly: Alzheimer disease pathology and cognitive status. J Neuropathol Exp Neurol. 2006;65:235–244. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
