Protein interacting with C kinase 1 (PICK1) reduces reinsertion rates of interaction partners sorted to Rab11-dependent slow recycling pathway
- PMID: 22303009
- PMCID: PMC3320979
- DOI: 10.1074/jbc.M111.294702
Protein interacting with C kinase 1 (PICK1) reduces reinsertion rates of interaction partners sorted to Rab11-dependent slow recycling pathway
Abstract
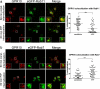
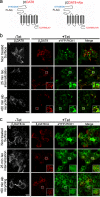
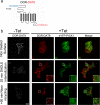
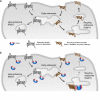
The scaffolding protein PICK1 (protein interacting with C kinase 1) contains an N-terminal PSD-95/Discs large/ZO-1 (PDZ) domain and a central lipid-binding Bin/amphiphysin/Rvs (BAR) domain. PICK1 is thought to regulate trafficking of its PDZ binding partners but different and even opposing functions have been suggested. Here, we apply ELISA-based assays and confocal microscopy in HEK293 cells with inducible PICK1 expression to assess in an isolated system the ability of PICK1 to regulate trafficking of natural and engineered PDZ binding partners. The dopamine transporter (DAT), which primarily sorts to degradation upon internalization, did not form perinuclear clusters with PICK1, and PICK1 did not affect DAT internalization/recycling. However, transfer of the PICK1-binding DAT C terminus to the β(2)-adrenergic receptor, which sorts to recycling upon internalization, led to formation of PICK1 co-clusters in Rab11-positive compartments. Furthermore, PICK1 inhibited Rab11-mediated recycling of the receptor in a BAR and PDZ domain-dependent manner. In contrast, transfer of the DAT C terminus to the δ-opioid receptor, which sorts to degradation, did not result in PICK1 co-clusters or any change in internalization/recycling. Further support for a role of PICK1 determined by its PDZ cargo was obtained for the PICK1 interaction partner prolactin-releasing peptide receptor (GPR10). GPR10 co-localized with Rab11 and clustered with PICK1 upon constitutive internalization but co-localized with the late endosomal marker Rab7 and did not cluster with PICK1 upon agonist-induced internalization. Our data suggest a selective role of PICK1 in clustering and reducing the recycling rates of PDZ domain binding partners sorted to the Rab11-dependent recycling pathway.
Figures




Similar articles
-
Membrane localization is critical for activation of the PICK1 BAR domain.Traffic. 2008 Aug;9(8):1327-43. doi: 10.1111/j.1600-0854.2008.00761.x. Epub 2008 May 8. Traffic. 2008. PMID: 18466293 Free PMC article.
-
Identification of a small-molecule inhibitor of the PICK1 PDZ domain that inhibits hippocampal LTP and LTD.Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2010 Jan 5;107(1):413-8. doi: 10.1073/pnas.0902225107. Epub 2009 Dec 14. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2010. PMID: 20018661 Free PMC article.
-
PICK1-ICA69 heteromeric BAR domain complex regulates synaptic targeting and surface expression of AMPA receptors.J Neurosci. 2007 Nov 21;27(47):12945-56. doi: 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.2040-07.2007. J Neurosci. 2007. PMID: 18032668 Free PMC article.
-
Structure and function of PICK1.Neurosignals. 2006-2007;15(4):190-201. doi: 10.1159/000098482. Epub 2007 Jan 11. Neurosignals. 2006. PMID: 17215589 Review.
-
Multiple faces of protein interacting with C kinase 1 (PICK1): Structure, function, and diseases.Neurochem Int. 2016 Sep;98:115-21. doi: 10.1016/j.neuint.2016.03.001. Epub 2016 Mar 9. Neurochem Int. 2016. PMID: 26970394 Review.
Cited by
-
Liposomal Encapsulated FSC231, a PICK1 Inhibitor, Prevents the Ischemia/Reperfusion-Induced Degradation of GluA2-Containing AMPA Receptors.Pharmaceutics. 2021 Apr 30;13(5):636. doi: 10.3390/pharmaceutics13050636. Pharmaceutics. 2021. PMID: 33946313 Free PMC article.
-
Membrane Binding and Modulation of the PDZ Domain of PICK1.Membranes (Basel). 2015 Oct 16;5(4):597-615. doi: 10.3390/membranes5040597. Membranes (Basel). 2015. PMID: 26501328 Free PMC article. Review.
-
A Computational Model for the AMPA Receptor Phosphorylation Master Switch Regulating Cerebellar Long-Term Depression.PLoS Comput Biol. 2016 Jan 25;12(1):e1004664. doi: 10.1371/journal.pcbi.1004664. eCollection 2016 Jan. PLoS Comput Biol. 2016. PMID: 26807999 Free PMC article.
-
A C-terminal PDZ domain-binding sequence is required for striatal distribution of the dopamine transporter.Nat Commun. 2013;4:1580. doi: 10.1038/ncomms2568. Nat Commun. 2013. PMID: 23481388 Free PMC article.
-
AMPA receptor pHluorin-GluA2 reports NMDA receptor-induced intracellular acidification in hippocampal neurons.Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2013 Aug 27;110(35):14426-31. doi: 10.1073/pnas.1312982110. Epub 2013 Aug 12. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2013. PMID: 23940334 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Dev K. K. (2007) PDZ domain protein-protein interactions: a case study with PICK1. Curr. Top. Med. Chem. 7, 3–20 - PubMed
-
- Xu J., Xia J. (2006) Structure and function of PICK1. Neurosignals 15, 190–201 - PubMed
-
- Staudinger J., Lu J., Olson E. N. (1997) Specific interaction of the PDZ domain protein PICK1 with the COOH terminus of protein kinase C-α. J. Biol. Chem. 272, 32019–32024 - PubMed
-
- Madsen K. L., Beuming T., Niv M. Y., Chang C. W., Dev K. K., Weinstein H., Gether U. (2005) Molecular determinants for the complex binding specificity of the PDZ domain in PICK1. J. Biol. Chem. 280, 20539–20548 - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

