The Arabidopsis circadian system
- PMID: 22303209
- PMCID: PMC3243369
- DOI: 10.1199/tab.0044
The Arabidopsis circadian system
Abstract
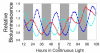
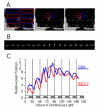
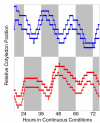
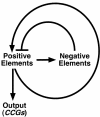
Rhythms with periods of approximately 24 hr are widespread in nature. Those that persist in constant conditions are termed circadian rhythms and reflect the activity of an endogenous biological clock. Plants, including Arabidopsis, are richly rhythmic. Expression analysis, most recently on a genomic scale, indicates that the Arabidopsis circadian clock regulates a number of key metabolic pathways and stress responses. A number of sensitive and high-throughput assays have been developed to monitor the Arabidopsis clock. These assays have facilitated the identification of components of plant circadian systems through genetic and molecular biological studies. Although much remains to be learned, the framework of the Arabidopsis circadian system is coming into focus.DedicationThis review is dedicated to the memory of DeLill Nasser, a wonderful mentor and an unwavering advocate of both Arabidopsis and circadian rhythms research.
Figures



References
-
- Adams J., Kelso R., Cooley L. The kelch repeat superfamily of proteins: propellers of cell function. Trends Cell Biol. 2000;101(1):17–24. - PubMed
-
- Ahmad M., Jarillo J. A., Smirnova O., Cashmore A. R. The CRY1 blue light photoreceptor of Arabidopsis interacts with phytochrome A in vitro. Mol. Cell. 1998;11(1):939–948. - PubMed
-
- Alabadí D., Oyama T., Yanovsky M. J., Harmon F. G., Más P., Kay S. A. Reciprocal regulation between TOC1 and LHY/CCA1 within the Arabidopsis circadian clock. Science. 2001;2931(1):880–883. - PubMed
-
- Aschoff J. Exogenous and endogenous components in circadian rhythms. Cold Spring Harbor Symposia on Quantitative Biology. 1960;1(1):11–28. XXV. - PubMed
-
- Barnes S. A., McGrath R. B., Chua N-H. Light signal transduction in plants. Trends Cell Biol. 1997;71(1):21–26. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
