PKCθ synergizes with TLR-dependent TRAF6 signaling pathway to upregulate MUC5AC mucin via CARMA1
- PMID: 22303480
- PMCID: PMC3267763
- DOI: 10.1371/journal.pone.0031049
PKCθ synergizes with TLR-dependent TRAF6 signaling pathway to upregulate MUC5AC mucin via CARMA1
Abstract
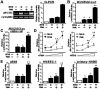
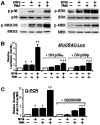
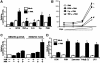
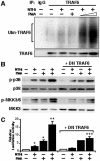
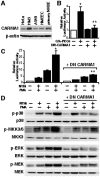
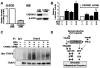
CARD-containing MAGUK protein 1 (CARMA1) plays a crucial role in regulating adaptive immune responses upon T-cell receptor (TCR) activation in T cells. Its role in regulating host mucosal innate immune response such as upregulation of mucin remains unknown. Here we show that CARMA1 acts as a key signaling mediator for synergistic upregulation of MUC5AC mucin by bacterium nontypeable Haemophilus influenzae (NTHi) and phorbol ester PMA in respiratory epithelial cells. NTHi-induced TLR-dependent TRAF6-MKK3-p38 MAPK signaling pathway synergizes with PKCθ-MEK-ERK signaling pathway. CARMA1 plays a crucial role in mediating this synergistic effect via TRAF6, thereby resulting in synergistic upregulation of MUC5AC mucin. Thus our study unveils a novel role for CARMA1 in mediating host mucosal innate immune response.
Conflict of interest statement
Figures

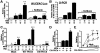
Similar articles
-
Epidermal growth factor receptor acts as a negative regulator for bacterium nontypeable Haemophilus influenzae-induced Toll-like receptor 2 expression via an Src-dependent p38 mitogen-activated protein kinase signaling pathway.J Biol Chem. 2005 Oct 28;280(43):36185-94. doi: 10.1074/jbc.M503941200. Epub 2005 Aug 22. J Biol Chem. 2005. PMID: 16115866
-
CKIP-1 is an intrinsic negative regulator of T-cell activation through an interaction with CARMA1.PLoS One. 2014 Jan 17;9(1):e85762. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0085762. eCollection 2014. PLoS One. 2014. PMID: 24465689 Free PMC article.
-
Induction of beta defensin 2 by NTHi requires TLR2 mediated MyD88 and IRAK-TRAF6-p38MAPK signaling pathway in human middle ear epithelial cells.BMC Infect Dis. 2008 Jun 25;8:87. doi: 10.1186/1471-2334-8-87. BMC Infect Dis. 2008. PMID: 18578886 Free PMC article.
-
Determining the destiny of NF-kappa B after TCR ligation: it's CARMA1.Mol Interv. 2002 Oct;2(6):356-60, 338. doi: 10.1124/mi.2.6.356. Mol Interv. 2002. PMID: 14993411 Review.
-
Exploitation of host epithelial signaling networks by respiratory bacterial pathogens.J Pharmacol Sci. 2003 Jan;91(1):1-7. doi: 10.1254/jphs.91.1. J Pharmacol Sci. 2003. PMID: 12686724 Review.
Cited by
-
Phloretin, an Apple Polyphenol, Inhibits Pathogen-Induced Mucin Overproduction.Mol Nutr Food Res. 2021 Jan;65(2):e2000658. doi: 10.1002/mnfr.202000658. Epub 2020 Dec 7. Mol Nutr Food Res. 2021. PMID: 33216464 Free PMC article.
-
The Novel PKCθ from Benchtop to Clinic.J Immunol Res. 2015;2015:348798. doi: 10.1155/2015/348798. Epub 2015 May 19. J Immunol Res. 2015. PMID: 26090489 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Home Dust Mites Promote MUC5AC Hyper-Expression by Modulating the sNASP/TRAF6 Axis in the Airway Epithelium.Int J Mol Sci. 2022 Aug 20;23(16):9405. doi: 10.3390/ijms23169405. Int J Mol Sci. 2022. PMID: 36012669 Free PMC article.
-
Regulation of ubiquitination in sepsis: from PAMP versus DAMP to peripheral inflammation and cell death.Front Immunol. 2024 Dec 10;15:1513206. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2024.1513206. eCollection 2024. Front Immunol. 2024. PMID: 39720715 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Liew FY, Xu D, Brint EK, O'Neill LA. Negative regulation of toll-like receptor-mediated immune responses. Nat Rev Immunol. 2005;5:446–458. - PubMed
-
- Dunne A, O'Neill LA. The interleukin-1 receptor/Toll-like receptor superfamily: signal transduction during inflammation and host defense. Sci STKE. 2003;2003:re3. - PubMed
-
- Akira S, Takeda K. Functions of toll-like receptors: lessons from KO mice. C R Biol. 2004;327:581–589. - PubMed
-
- Beutler B. Inferences, questions and possibilities in Toll-like receptor signalling. Nature. 2004;430:257–263. - PubMed
-
- Jono H, Shuto T, Xu H, Kai H, Lim DJ, et al. Transforming growth factor-beta -Smad signaling pathway cooperates with NF-kappa B to mediate nontypeable Haemophilus influenzae-induced MUC2 mucin transcription. J Biol Chem. 2002;277:45547–45557. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

