Amsacrine as a topoisomerase II poison: importance of drug-DNA interactions
- PMID: 22304499
- PMCID: PMC3289736
- DOI: 10.1021/bi201159b
Amsacrine as a topoisomerase II poison: importance of drug-DNA interactions
Abstract
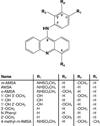
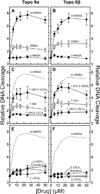
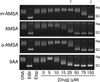
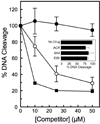
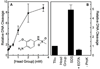
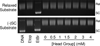
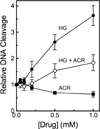
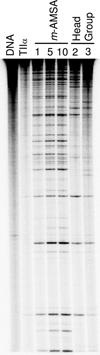
Amsacrine (m-AMSA) is an anticancer agent that displays activity against refractory acute leukemias as well as Hodgkin's and non-Hodgkin's lymphomas. The drug is comprised of an intercalative acridine moiety coupled to a 4'-amino-methanesulfon-m-anisidide headgroup. m-AMSA is historically significant in that it was the first drug demonstrated to function as a topoisomerase II poison. Although m-AMSA was designed as a DNA binding agent, the ability to intercalate does not appear to be the sole determinant of drug activity. Therefore, to more fully analyze structure-function relationships and the role of DNA binding in the action of m-AMSA, we analyzed a series of derivatives for the ability to enhance DNA cleavage mediated by human topoisomerase IIα and topoisomerase IIβ and to intercalate DNA. Results indicate that the 3'-methoxy (m-AMSA) positively affects drug function, potentially by restricting the rotation of the headgroup in a favorable orientation. Shifting the methoxy to the 2'-position (o-AMSA), which abrogates drug function, appears to increase the degree of rotational freedom of the headgroup and may impair interactions of the 1'-substituent or other portions of the headgroup within the ternary complex. Finally, the nonintercalative m-AMSA headgroup enhanced enzyme-mediated DNA cleavage when it was detached from the acridine moiety, albeit with 100-fold lower affinity. Taken together, our results suggest that much of the activity and specificity of m-AMSA as a topoisomerase II poison is embodied in the headgroup, while DNA intercalation is used primarily to increase the affinity of m-AMSA for the topoisomerase II-DNA cleavage complex.
Figures




References
-
- National Cancer Institute. Clinical Trials. 2011 http://www.cancer.gov/clinicaltrials/search/results?protocolsearchid=923....
-
- Jehn U, Heinemann V. New drugs in the treatment of acute and chronic leukemia with some emphasis on m-AMSA. Anticancer Res. 1991;11:705–711. - PubMed
-
- Kell J. Treatment of relapsed acute myeloid leukaemia. Rev. Recent Clin. Trials. 2006;1:103–111. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

