A structure-based mechanism for Arf1-dependent recruitment of coatomer to membranes
- PMID: 22304919
- PMCID: PMC3285272
- DOI: 10.1016/j.cell.2012.01.015
A structure-based mechanism for Arf1-dependent recruitment of coatomer to membranes
Abstract
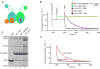
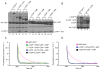
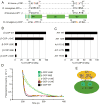
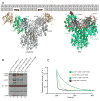
Budding of COPI-coated vesicles from Golgi membranes requires an Arf family G protein and the coatomer complex recruited from cytosol. Arf is also required with coatomer-related clathrin adaptor complexes to bud vesicles from the trans-Golgi network and endosomal compartments. To understand the structural basis for Arf-dependent recruitment of a vesicular coat to the membrane, we determined the structure of Arf1 bound to the γζ-COP subcomplex of coatomer. Structure-guided biochemical analysis reveals that a second Arf1-GTP molecule binds to βδ-COP at a site common to the γ- and β-COP subunits. The Arf1-binding sites on coatomer are spatially related to PtdIns4,5P(2)-binding sites on the endocytic AP2 complex, providing evidence that the orientation of membrane binding is general for this class of vesicular coat proteins. A bivalent GTP-dependent binding mode has implications for the dynamics of coatomer interaction with the Golgi and for the selection of cargo molecules.
Copyright © 2012 Elsevier Inc. All rights reserved.
Figures
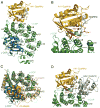

References
-
- Ahmadian MR, Hoffman U, Goody RS, Wittinghofer A. Individual rate constants for the interaction of Ras proteins with GTPase-activating proteins determined by fluorescence spectroscopy. Biochemistry. 1997;36:4535–4541. - PubMed
-
- Amor JC, Harrison DH, Kahn RA, Ringe D. Structure of the human ADP-ribosylation factor 1 complexed with GDP. Nature. 1994;372:704–708. - PubMed
-
- Antonny B, Beraud-Dufour S, Chardin P, Chabre M. N-terminal hydrophobic residues of the G-protein ADP-ribosylation factor-1 insert into membrane phospholipids upon GDP to GTP exchange. Biochemistry. 1997;36:4675–4684. - PubMed
-
- Barlowe C, Orci L, Yeung T, Hosobuchi M, Hamamoto S, Salama N, Rexach MF, Ravazzola M, Amherdt M, Schekman R. COPII: a membrane coat formed by Sec proteins that drive vesicle budding from the endoplasmic reticulum. Cell. 1994;77:895–907. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Associated data
- Actions
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials

