Fundamentals of transcranial electric and magnetic stimulation dose: definition, selection, and reporting practices
- PMID: 22305345
- PMCID: PMC3346863
- DOI: 10.1016/j.brs.2011.10.001
Fundamentals of transcranial electric and magnetic stimulation dose: definition, selection, and reporting practices
Abstract
Background: The growing use of transcranial electric and magnetic (EM) brain stimulation in basic research and in clinical applications necessitates a clear understanding of what constitutes the dose of EM stimulation and how it should be reported.
Methods: This paper provides fundamental definitions and principles for reporting of dose that encompass any transcranial EM brain stimulation protocol.
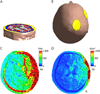
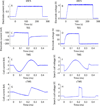
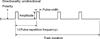
Results: The biologic effects of EM stimulation are mediated through an electromagnetic field injected (via electric stimulation) or induced (via magnetic stimulation) in the body. Therefore, transcranial EM stimulation dose ought to be defined by all parameters of the stimulation device that affect the electromagnetic field generated in the body, including the stimulation electrode or coil configuration parameters: shape, size, position, and electrical properties, as well as the electrode or coil current (or voltage) waveform parameters: pulse shape, amplitude, width, polarity, and repetition frequency; duration of and interval between bursts or trains of pulses; total number of pulses; and interval between stimulation sessions and total number of sessions. Knowledge of the electromagnetic field generated in the body may not be sufficient but is necessary to understand the biologic effects of EM stimulation.
Conclusions: We believe that reporting of EM stimulation dose should be guided by the principle of reproducibility: sufficient information about the stimulation parameters should be provided so that the dose can be replicated.
Copyright © 2012 Elsevier Inc. All rights reserved.
Figures

References
-
- Bikson M, Bulow P, Stiller JW, et al. Transcranial direct current stimulation for major depression: a general system for quantifying transcranial electrotherapy dosage. Curr Treat Options Neurol. 2008;10:377–385. - PubMed
-
- Nitsche MA, Cohen LG, Wassermann EM, et al. Transcranial direct current stimulation: State of the art 2008. Brain Stimul. 2008;1:206–223. - PubMed
-
- Weiner RD, Weaver LA, Jr, Sackeim HA. Reporting of technical parameters in ECT publications: recommendations for authors. Convuls Ther. 1988;4:88–91. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
- NIMH 41771-00-01/PHS HHS/United States
- 5U01MH084241-02/MH/NIMH NIH HHS/United States
- MO1 RR01032/RR/NCRR NIH HHS/United States
- K24 RR018875/RR/NCRR NIH HHS/United States
- UL1 RR025758/RR/NCRR NIH HHS/United States
- NIGMS 41341-03-30/PHS HHS/United States
- R01 MH091083/MH/NIMH NIH HHS/United States
- U01 MH084241/MH/NIMH NIH HHS/United States
- R01MH091083/MH/NIMH NIH HHS/United States
- M01 RR001032/RR/NCRR NIH HHS/United States
- 5R01MH060884-09/MH/NIMH NIH HHS/United States
- R01MH091083-01/MH/NIMH NIH HHS/United States
- R01 MH060884/MH/NIMH NIH HHS/United States
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

