Mechanisms and predictors of mitral regurgitation after high-risk myocardial infarction
- PMID: 22305962
- PMCID: PMC3501447
- DOI: 10.1016/j.echo.2012.01.006
Mechanisms and predictors of mitral regurgitation after high-risk myocardial infarction
Abstract
Background: Mitral regurgitation (MR) has been associated with adverse outcomes after myocardial infarction (MI). Without structural valve disease, functional MR has been related to left ventricular (LV) remodeling and geometric deformation of the mitral apparatus. The aims of this study were to elucidate the mechanistic components of MR after high-risk MI and to identify predictors of MR progression during follow-up.
Methods: The Valsartan in Acute Myocardial Infarction Echo substudy prospectively enrolled 610 patients with LV dysfunction, heart failure, or both after MI. MR at baseline, 1 month, and 20 months was quantified by mapping jet expansion in the left atrium in 341 patients with good-quality echocardiograms. Indices of LV remodeling, left atrial size, and diastolic function and parameters of mitral valve deformation, including tenting area, coaptation depth, anterior leaflet concavity, annular diameters, and contractility, were assessed and related to baseline MR. The progression of MR was further analyzed, and predictors of worsening among the baseline characteristics were identified.
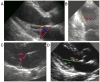
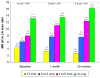
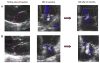
Results: Tenting area, coaptation depth, annular dilatation, and left atrial size were all associated with the degree of baseline MR. Tenting area was the only significant and independent predictor of worsening MR; a tenting area of 4 cm(2) was a useful cutoff to identify worsening of MR after MI and moderate to severe MR after 20 months.
Conclusions: Increased mitral tenting and larger mitral annular area are determinants of MR degree at baseline, and tenting area is an independent predictor of progression of MR after MI. Although LV remodeling itself contributes to ischemic MR, this influence is directly dependent on alterations in mitral geometry.
Copyright © 2012 American Society of Echocardiography. Published by Mosby, Inc. All rights reserved.
Figures

References
-
- Amigoni M, Meris A, Thune JJ, Mangalat D, Skali H, Bourgoun M, et al. Mitral regurgitation in myocardial infarction complicated by heart failure, left ventricular dysfunction, or both: prognostic significance and relation to ventricular size and function. Eur Heart J. 2007;28:326–33. - PubMed
-
- Lamas GA, Mitchell GF, Flaker GC, Smith SC, Jr, Gersh BJ, Basta L, et al. Survival and Ventricular Enlargement Investigators. Clinical significance of mitral regurgitation after acute myocardial infarction. Circulation. 1997;96:827–33. - PubMed
-
- Grigioni F, Enriquez-Sarano M, Zehr K, Bailey K, Tajik A. Ischemic mitral regurgitation: long-term outcome and prognostic implications with quantitative Doppler assessment. Circulation. 2001;103:1759–64. - PubMed
-
- Bursi F, Enriquez-Sarano M, Nkomo VT, Jacobsen SJ, Weston SA, Meverden RA, et al. Heart failure and death after myocardial infarction in the community: the emerging role of mitral regurgitation. Circulation. 2005;11:295–301. - PubMed
-
- Grigioni F, Detaint D, Avierinos JF, Scott C, Tajik J, Enriquez-Sarano M. Contribution of ischemic mitral regurgitation to congestive heart failure after myocardial infarction. J Am Coll Cardiol. 2005;45:260–77. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

