Small-angle X-ray scattering and single-molecule FRET spectroscopy produce highly divergent views of the low-denaturant unfolded state
- PMID: 22306460
- PMCID: PMC3523729
- DOI: 10.1016/j.jmb.2012.01.016
Small-angle X-ray scattering and single-molecule FRET spectroscopy produce highly divergent views of the low-denaturant unfolded state
Abstract
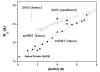
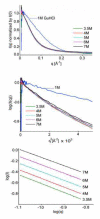
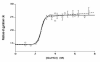
The results of more than a dozen single-molecule Förster resonance energy transfer (smFRET) experiments suggest that chemically unfolded polypeptides invariably collapse from an expanded random coil to more compact dimensions as the denaturant concentration is reduced. In sharp contrast, small-angle X-ray scattering (SAXS) studies suggest that, at least for single-domain proteins at non-zero denaturant concentrations, such compaction may be rare. Here, we explore this discrepancy by studying protein L, a protein previously studied by SAXS (at 5 °C), which suggested fixed unfolded-state dimensions from 1.4 to 5 M guanidine hydrochloride (GuHCl), and by smFRET (at 25 °C), which suggested that, in contrast, the chain contracts by 15-30% over this same denaturant range. Repeating the earlier SAXS study under the same conditions employed in the smFRET studies, we observe little, if any, evidence that the unfolded state of protein L contracts as the concentration of GuHCl is reduced. For example, scattering profiles (and thus the shape and dimensions) collected within ∼4 ms after dilution to as low as 0.67 M GuHCl are effectively indistinguishable from those observed at equilibrium at higher denaturant. Our results thus argue that the disagreement between SAXS and smFRET is statistically significant and that the experimental evidence in favor of obligate polypeptide collapse at low denaturant cannot be considered conclusive yet.
Copyright © 2012 Elsevier Ltd. All rights reserved.
Figures

References
-
- McCarney ER, Kohn JE, Plaxco KW. Is there or isn’t there? The case for (and against) residual structure in chemically denatured proteins. Crit Rev Bioch Mol Biol. 2005;40:181–189. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
- GM55694/GM/NIGMS NIH HHS/United States
- R01 GM080515/GM/NIGMS NIH HHS/United States
- P41 RR008630/RR/NCRR NIH HHS/United States
- R01 GM055694/GM/NIGMS NIH HHS/United States
- EB002046/EB/NIBIB NIH HHS/United States
- GM080515/GM/NIGMS NIH HHS/United States
- T32 GM008267/GM/NIGMS NIH HHS/United States
- GM-008267/GM/NIGMS NIH HHS/United States
- RR-08630/RR/NCRR NIH HHS/United States
- DMR-0225180/GM/NIGMS NIH HHS/United States
- R29 GM055694/GM/NIGMS NIH HHS/United States
- P41 RR001209/RR/NCRR NIH HHS/United States
- R01 EB002046/EB/NIBIB NIH HHS/United States
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

