The Hill model for binding myosin S1 to regulated actin is not equivalent to the McKillop-Geeves model
- PMID: 22306466
- PMCID: PMC3306264
- DOI: 10.1016/j.jmb.2012.01.011
The Hill model for binding myosin S1 to regulated actin is not equivalent to the McKillop-Geeves model
Abstract
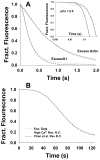
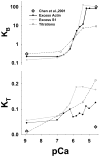
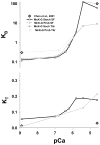
The Hill two-state cooperativity model and the McKillop-Geeves (McK-G) three-state model predict very similar binding traces of myosin subfragment 1 (S1) binding to regulated actin filaments in the presence and absence of calcium, and both fit the experimental data reasonably well [Chen et al., Biophys. J., 80, 2338-2349]. Here, we compared the Hill model and the McK-G model for binding myosin S1 to regulated actin against three sets of experimental data: the titration of regulated actin with S1 and the kinetics of S1 binding of regulated actin with either excess S1 to actin or excess actin to S1. Each data set was collected for a wide range of specified calcium concentrations. Both models were able to generate reasonable fits to the time course data and to titration data. The McK-G model can fit all three data sets with the same calcium-concentration-sensitive parameters. Only K(B) and K(T) show significant calcium dependence, and the parameters have a classic pCa curve. A unique set of the Hill model parameters was extremely difficult to estimate from the best fits of multiple sets of data. In summary, the McK-G cooperativity model more uniquely resolves parameters estimated from kinetic and titration data than the Hill model, predicts a sigmoidal dependence of key parameters with calcium concentration, and is simpler and more suitable for practical use.
Copyright © 2012 Elsevier Ltd. All rights reserved.
Figures






References
-
- Vibert P, Craig R, Lehman W. Steric-model for activation of muscle thin filaments. J Mol Biol. 1997;266:8–14. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

