Differential confounding of rare and common variants in spatially structured populations
- PMID: 22306651
- PMCID: PMC3303124
- DOI: 10.1038/ng.1074
Differential confounding of rare and common variants in spatially structured populations
Abstract
Well-powered genome-wide association studies, now made possible through advances in technology and large-scale collaborative projects, promise to characterize the contribution of rare variants to complex traits and disease. However, while population structure is a known confounder of association studies, it remains unknown whether methods developed to control stratification are equally effective for rare variants. Here, we demonstrate that rare variants can show a stratification that is systematically different from, and typically stronger than, common variants, and this is not necessarily corrected by existing methods. We show that the same process leads to inflation for load-based tests and can obscure signals at truly associated variants. Furthermore, we show that populations can display spatial structure in rare variants, even when Wright's fixation index F(ST) is low, but that allele frequency-dependent metrics of allele sharing can reveal localized stratification. These results underscore the importance of collecting and integrating spatial information in the genetic analysis of complex traits.
Figures
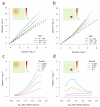
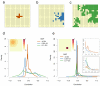
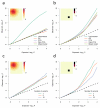
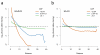
Comment in
-
FaST-LMM-Select for addressing confounding from spatial structure and rare variants.Nat Genet. 2013 May;45(5):470-1. doi: 10.1038/ng.2620. Nat Genet. 2013. PMID: 23619783 No abstract available.
-
Reply to: "FaST-LMM-Select for addressing confounding from spatial structure and rare variants".Nat Genet. 2013 May;45(5):471. doi: 10.1038/ng.2619. Nat Genet. 2013. PMID: 23619784 No abstract available.
References
-
- Cohen JC, et al. Multiple rare alleles contribute to low plasma levels of HDL cholesterol. Science. 2004;305:869–872. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Miscellaneous

