A role for mechanosensitive channels in chloroplast and bacterial fission
- PMID: 22307046
- PMCID: PMC3405697
- DOI: 10.4161/psb.18735
A role for mechanosensitive channels in chloroplast and bacterial fission
Abstract
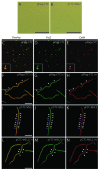
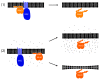
The division site in both chloroplasts and bacteria is established by the medial placement of the FtsZ ring, a process that is in part regulated by the evolutionarily conserved components of the Min system. We recently showed that mechanosensitive ion channels influence FtsZ ring assembly in both Arabidopsis thaliana chloroplasts and in Escherichia coli; in chloroplasts they do so through the same genetic pathway as the Min system. Here we describe the effect of heterologous expression of the Arabidopsis MS channel homolog MSL2 on FtsZ ring placement in E. coli. We also discuss possible molecular mechanisms by which MS channels might influence chloroplast or bacterial division.
Figures
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
