Dynamics of the linuron hydrolase libA gene pool size in response to linuron application and environmental perturbations in agricultural soil and on-farm biopurification systems
- PMID: 22307296
- PMCID: PMC3318807
- DOI: 10.1128/AEM.06991-11
Dynamics of the linuron hydrolase libA gene pool size in response to linuron application and environmental perturbations in agricultural soil and on-farm biopurification systems
Abstract
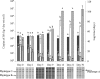
libA, a gene encoding a novel type of linuron hydrolase, was recently identified in the linuron-mineralizing Variovorax sp. strain SRS16. In order to assess the contribution of libA to linuron degradation in environmental settings, libA abundance was monitored in response to the application of linuron and to environmental perturbations in agricultural soil microcosms and microcosms simulating the matrix of on-farm biopurification systems. libA numbers were measured by real-time PCR and linked to reported data of Variovorax community composition and linuron mineralization capacity. In the soil microcosms and one biopurification system setup, libA numbers responded to the application of linuron and environmental changes in congruency with the modulation of linuron mineralization capacity and the occurrence of a particular Variovorax phylotype (phylotype A). However, in another biopurification system setup, no such correlations were found. Our data suggest that in the simulated environmental settings, the occurrence of libA can be linked to the linuron mineralization capacity and that libA is primarily hosted by Variovorax phylotype A strains. However, the results also suggest that, apart from libA, other, as-yet-unknown isofunctional genes play an important role in linuron mineralization in the environment.
Figures



References
-
- Baelum J, et al. 2008. Direct analysis of tfdA gene expression by indigenous bacteria in phenoxy acid amended agricultural soil. ISME J. 2:677–687 - PubMed
-
- Beller HR, Kane SR, Legler TC, Alvarez PJ. 2002. A real-time polymerase chain reaction method for monitoring anaerobic, hydrocarbon-degrading bacteria based on a catabolic gene. Environ. Sci. Technol. 36:3977–3984 - PubMed
-
- Bers K, et al. 2011. A molecular toolbox to estimate the number and diversity of Variovorax in the environment: application in soils treated with the phenylurea herbicide linuron. FEMS Microbiol. Ecol. 76:14–25 - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

