Enhanced activation of RVLM-projecting PVN neurons in rats with chronic heart failure
- PMID: 22307669
- PMCID: PMC3330797
- DOI: 10.1152/ajpheart.00722.2011
Enhanced activation of RVLM-projecting PVN neurons in rats with chronic heart failure
Abstract
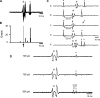
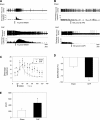
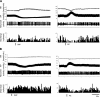
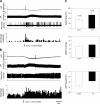
Previous studies have indicated that there is increased activation of the paraventricular nucleus (PVN) in rats with chronic heart failure (CHF); however, it is not clear if the preautonomic neurons within the PVN are specifically overactive. Also, it is not known if these neurons have altered responses to baroreceptor or osmotic challenges. Experiments were conducted in rats with CHF (6-8 wk after coronary artery ligation). Spontaneously active neurons were recorded in the PVN, of which 36% were antidromically activated from the rostral ventrolateral medulla (RVLM). The baseline discharge rate in RVLM-projecting PVN (PVN-RVLM) neurons from CHF rats was significantly greater than in sham-operated (sham) rats (6.0 ± 0.6 vs. 2.6 ± 0.3 spikes/s, P < 0.05). Picoinjection of the N-methyl-D-aspartate (NMDA) receptor antagonist D,L-2-amino-5-phosphonovaleric acid significantly decreased the basal discharge of PVN-RVLM neurons by 80% in CHF rats compared with 37% in sham rats. Fifty-two percent of spontaneously active PVN-RVLM neurons responded to changes in the mean arterial pressure (MAP). The changes in discharge rate in PVN-RVLM neurons after a reduction in MAP (+52 ± 7% vs. +184 ± 61%) or an increase in MAP (-42 ± 8% vs. -71 ± 6%) were significantly attenuated in rats with CHF compared with sham rats. Most PVN-RVLM neurons (63%), including all barosensitive PVN-RVLM neurons, were excited by an internal carotid artery injection of hypertonic NaCl (2.1 osmol/l), whereas a smaller number (7%) were inhibited. The increase in discharge rate in PVN-RVLM neurons to hypertonic stimulation was significantly enhanced in rats with CHF compared with sham rats (134 ± 15% vs. 92 ± 13%). Taken together, these data suggest that PVN-RVLM neurons are more active under basal conditions and this overactivation is mediated by an enhanced glutamatergic tone in rats with CHF. Furthermore, this enhanced activation of PVN-RVLM neurons may contribute to the altered responses to baroreceptor and osmotic challenges observed during CHF.
Figures




Similar articles
-
Activation of afferent renal nerves modulates RVLM-projecting PVN neurons.Am J Physiol Heart Circ Physiol. 2015 May 1;308(9):H1103-11. doi: 10.1152/ajpheart.00862.2014. Epub 2015 Jan 30. Am J Physiol Heart Circ Physiol. 2015. PMID: 25637549 Free PMC article.
-
Tonic glutamatergic input in the rostral ventrolateral medulla is increased in rats with chronic heart failure.Hypertension. 2009 Feb;53(2):370-4. doi: 10.1161/HYPERTENSIONAHA.108.122598. Epub 2008 Nov 24. Hypertension. 2009. PMID: 19029485 Free PMC article.
-
NMDA-mediated increase in renal sympathetic nerve discharge within the PVN: role of nitric oxide.Am J Physiol Heart Circ Physiol. 2001 Dec;281(6):H2328-36. doi: 10.1152/ajpheart.2001.281.6.H2328. Am J Physiol Heart Circ Physiol. 2001. PMID: 11709399
-
Sympathoexcitation by hypothalamic paraventricular nucleus neurons projecting to the rostral ventrolateral medulla.J Physiol. 2018 Oct;596(19):4581-4595. doi: 10.1113/JP276223. Epub 2018 Aug 18. J Physiol. 2018. PMID: 30019338 Free PMC article.
-
In vivo discharge properties of hypothalamic paraventricular nucleus neurons with axonal projections to the rostral ventrolateral medulla.J Neurophysiol. 2010 Jan;103(1):4-15. doi: 10.1152/jn.00094.2009. Epub 2009 Nov 4. J Neurophysiol. 2010. PMID: 19889858 Free PMC article.
Cited by
-
Electroacupuncture Regulates Sympathetic Nerve Through the NTSGlu-RVLM Circuit to Relieve Spontaneous Pain in SNI Rats.CNS Neurosci Ther. 2025 Mar;31(3):e70327. doi: 10.1111/cns.70327. CNS Neurosci Ther. 2025. PMID: 40150822 Free PMC article.
-
Navigating Central Oxytocin Transport: Known Realms and Uncharted Territories.Neuroscientist. 2025 Jun;31(3):234-261. doi: 10.1177/10738584241268754. Epub 2024 Aug 7. Neuroscientist. 2025. PMID: 39113465 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Thalamic dopaminergic neurons projects to the paraventricular nucleus-rostral ventrolateral medulla/C1 neural circuit.Anat Rec (Hoboken). 2017 Jul;300(7):1307-1314. doi: 10.1002/ar.23528. Epub 2017 Apr 10. Anat Rec (Hoboken). 2017. PMID: 27981779 Free PMC article.
-
Systemic Sympathoexcitation Was Associated with Paraventricular Hypothalamic Phosphorylation of Synaptic CaMKIIα and MAPK/ErK.Front Neurosci. 2017 Aug 3;11:447. doi: 10.3389/fnins.2017.00447. eCollection 2017. Front Neurosci. 2017. PMID: 28824368 Free PMC article.
-
Calcineurin Controls Hypothalamic NMDA Receptor Activity and Sympathetic Outflow.Circ Res. 2022 Aug 5;131(4):361-363. doi: 10.1161/CIRCRESAHA.122.321581. Epub 2022 Aug 4. Circ Res. 2022. PMID: 35926008 Free PMC article. No abstract available.
References
-
- Akaoka H, Saunier CF, Chergui K, Charlety P, Buda M, Chouvet G. Combining in vivo volume-controlled pressure microejection with extracellular unit recording. J Neurosci Methods 42: 119–128, 1992 - PubMed
-
- Armstrong WE, Warach S, Hatton GI, McNeill TH. Subnuclei in the rat hypothalamic paraventricular nucleus: a cytoarchitectural, horseradish peroxidase and immunocytochemical analysis. Neuroscience 5: 1931–1958, 1980 - PubMed
-
- Badoer E. Hypothalamic paraventricular nucleus and cardiovascular regulation. Clin Exp Pharmacol Physiol 28: 95–99, 2001 - PubMed
-
- Chen QH, Toney GM. AT1-receptor blockade in the hypothalamic PVN reduces central hyperosmolality-induced renal sympathoexcitation. Am J Physiol Regul Integr Comp Physiol 281: R1844–R1853, 2001 - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

