Increased PAI-1 in females compared with males is protective for abdominal aortic aneurysm formation in a rodent model
- PMID: 22307671
- PMCID: PMC3330791
- DOI: 10.1152/ajpheart.00620.2011
Increased PAI-1 in females compared with males is protective for abdominal aortic aneurysm formation in a rodent model
Abstract
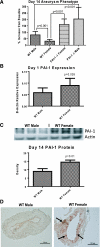
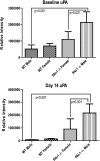
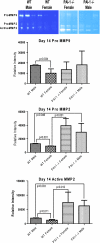
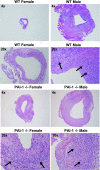
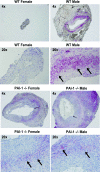
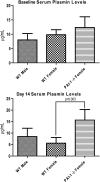
The serine proteases, along with their inhibitor plasmin activator inhibitor-1 (PAI-1), have been shown to play a role in abdominal aortic aneurysm (AAA) formation. The aim of this study is to determine if PAI-1 may be a protective factor for AAA formation and partially responsible for the gender difference observed in AAAs. Male and female wild-type (WT) C57BL/6 and PAI-1(-/-) mice 8-12 wk of age underwent aortic perfusion with porcine pancreatic elastase. Animals were harvested 14 days following perfusion and analyzed for phenotype, PAI-1 protein levels, and matrix metalloproteinase (MMP)-9 and -2 activity. WT males had an average increase in aortic diameter of 80%, whereas females only increased 32% (P < 0.001). PAI-1(-/-) males increased 204% and females 161%, significantly more than their WT counterparts (P < 0.001). Western blot revealed 61% higher PAI-1 protein levels in the WT females compared with the WT males (P = 0.01). Zymography revealed higher levels of pro-MMP-2 and active MMP-2 in the PAI-1(-/-) males and females compared with their WT counterparts. PAI-1(-/-) females had significantly higher serum plasmin levels compared with WT females (P = 0.003). In conclusion, WT female mice are protected from aneurysm formation and have higher levels of PAI-1 compared with males during experimental aneurysm formation. Additionally, both male and female PAI-1(-/-) animals develop significantly larger aneurysms than WT animals, correlating with higher pro- and active MMP-2 levels. These findings suggest that PAI-1 is protective for aneurysm formation in the elastase model of AAA and plays a role in the gender differences seen in AAA formation.
Figures
References
-
- Allaire E, Hasenstab D, Kenagy R, Starcher B, Clowes M, Clowes A. Prevention of aneurysm development and rupture by local overexpression of plasminogen activator inhibitor-1. Circulation 98: 249–255, 1998. - PubMed
-
- Baramova E, Bajou K, Remacle A, L'Hoir C, Krell H, Weidle U, Noel A, Foidart J. Involvement of PA/plasmin system in the processing of pre-MMP-9 and in the second step of pro-MMP-2 activation. FEBS Lett 405: 157–162, 1997. - PubMed
-
- Brown N. Theraputic potential of plasminogen activator inhibitor-1 inhibitors. Ther Adv Cardiovasc Dis 4: 315–324, 2010. - PubMed
-
- Carmeliet P, Moons L, Lijnen R, Baes M, Lemaitre V, Tipping P, Drew A, Eeckhout Y, Shapiro S, Lupu F, Collen D. Urokinase-generated plasmin activates matrix metalloproteinases during aneurysm formation. Nat Gen 17: 439–444, 1997. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Miscellaneous

