The amyloid-β isoform pattern in cerebrospinal fluid in familial PSEN1 M139T- and L286P-associated Alzheimer's disease
- PMID: 22307680
- PMCID: PMC3493058
- DOI: 10.3892/mmr.2012.774
The amyloid-β isoform pattern in cerebrospinal fluid in familial PSEN1 M139T- and L286P-associated Alzheimer's disease
Abstract
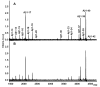
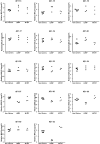
There are several familial forms of Alzheimer's disease (AD) most of which are caused by mutations in the genes that encode the presenilin enzymes involved in the production of amyloid-β (Aβ) from the amyloid precursor protein (APP). In AD, Aβ forms fibrils that are deposited in the brain as plaques. Much of the fibrillar Aβ found in the plaques consists of the 42 amino acid form of Aβ (Aβ1-42) and it is now widely accepted that Aβ is related to the pathogenesis of AD and that Aβ may both impair memory and be neurotoxic. In human cerebrospinal fluid (CSF) several C- and N-terminally truncated Aβ isoforms have been detected and their relative abundance pattern is thought to reflect the production and clearance of Aβ. By using immunoprecipitation and mass spectrometry, we have previously demonstrated that carriers of the familial AD (FAD)-associated PSEN1 A431E mutation have low CSF levels of C-terminally truncated Aβ isoforms shorter than Aβ1-40. Here we replicate this finding in symptomatic carriers of the FAD-causing PSEN1 L286P mutation. Furthermore, we show that preclinical carriers of the PSEN1 M139T mutation may overexpress Aβ1-42 suggesting that this particular mutation may cause AD by stimulating γ-secretase-mediated cleavage at amino acid 42 in the Aβ sequence.
Figures
References
-
- Hardy JA, Higgins GA. Alzheimer's disease: the amyloid cascade hypothesis. Science. 1992;256:184–185. - PubMed
-
- Lemere CA, Blusztajn JK, Yamaguchi H, Wisniewski T, Saido TC, Selkoe DJ. Sequence of deposition of heterogeneous amyloid beta-peptides and APO E in Down syndrome: implications for initial events in amyloid plaque formation. Neurobiol Dis. 1996;3:16–32. - PubMed
-
- Rovelet-Lecrux A, Hannequin D, Raux G, et al. APP locus duplication causes autosomal dominant early-onset Alzheimer disease with cerebral amyloid angiopathy. Nat Genet. 2006;38:24–26. - PubMed
-
- Beher D, Wrigley JD, Owens AP, Shearman MS. Generation of C-terminally truncated amyloid-beta peptides is dependent on gamma-secretase activity. J Neurochem. 2002;82:563–575. - PubMed
-
- Portelius E, Price E, Brinkmalm G, et al. A novel pathway for amyloid precursor protein processing. Neurobiol Aging. 2011;32:1090–1098. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

