Prospective cohort study of radiotherapy with concomitant and adjuvant temozolomide chemotherapy for glioblastoma patients with no or minimal residual enhancing tumor load after surgery
- PMID: 22307805
- PMCID: PMC3337400
- DOI: 10.1007/s11060-012-0798-3
Prospective cohort study of radiotherapy with concomitant and adjuvant temozolomide chemotherapy for glioblastoma patients with no or minimal residual enhancing tumor load after surgery
Abstract
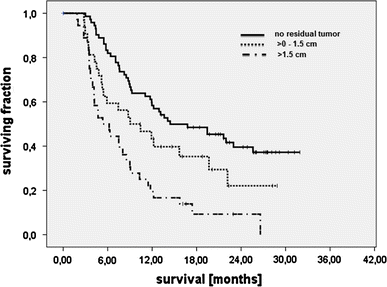
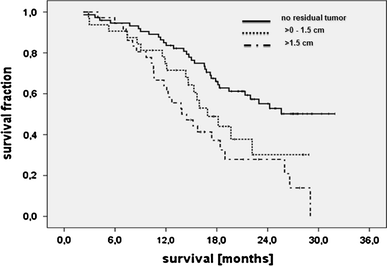
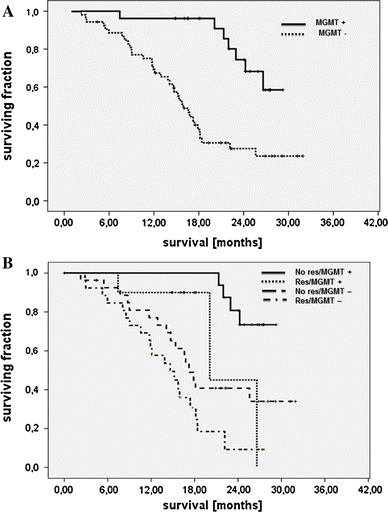
Survival of glioblastoma patients has been linked to the completeness of surgical resection. Available data, however, were generated with adjuvant radiotherapy. Data confirming that extensive cytoreduction remains beneficial to patients treated with the current standard, concomitant temozolomide radiochemotherapy, are limited. We therefore analyzed the efficacy of radiochemotherapy for patients with little or no residual tumor after surgery. In this prospective, non-interventional multicenter cohort study, entry criteria were histological diagnosis of glioblastoma, small enhancing or no residual tumor on post-operative MRI, and intended temozolomide radiochemotherapy. The primary study objective was progression-free survival; secondary study objectives were survival and toxicity. Furthermore, the prognostic value of O6-methylguanine-DNA methyltransferase (MGMT) promoter methylation was investigated in a subgroup of patients. One-hundred and eighty patients were enrolled. Fourteen were excluded by patient request or failure to initiate radiochemotherapy. Twenty-three patients had non-evaluable post-operative imaging. Thus, 143 patients qualified for analysis, with 107 patients having residual tumor diameters ≤1.5 cm. Median follow-up was 24.0 months. Median survival or patients without residual enhancing tumor exceeded the follow-up period. Median survival was 16.9 months for 32 patients with residual tumor diameters >0 to ≤1.5 cm (95% CI: 13.3-20.5, p = 0.039), and 13.9 months (10.3-17.5, overall p < 0.001) for 36 patients with residual tumor diameters >1.5 cm. Patient age at diagnosis and extent of resection were independently associated with survival. Patients with MGMT promoter methylated tumors and complete resection made the best prognosis. Completeness of resection acts synergistically with concomitant and adjuvant radiochemotherapy, especially in patients with MGMT promoter methylation.
Figures
References
-
- Stummer W, Pichlmeier U, Meinel T, Wiestler OD, Zanella F, Reulen HJ. ALA-Glioma Study Group. Fluorescence-guided surgery with 5-aminolevulinic acid for resection of malignant glioma: a randomised controlled multicentre phase III trial. Lancet Oncol. 2006;7:392–401. doi: 10.1016/S1470-2045(06)70665-9. - DOI - PubMed
-
- Stupp R, Hegi ME, Mason WP, van den Bent MJ, Taphoorn MJ, Janzer RC, et al. Effects of radiotherapy with concomitant and adjuvant temozolomide versus radiotherapy alone on survival in glioblastoma in a randomised phase III study: 5-year analysis of the EORTC-NCIC trial. Lancet Oncol. 2009;10:459–466. doi: 10.1016/S1470-2045(09)70025-7. - DOI - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Research Materials

