TRESK gene recombinant adenovirus vector inhibits capsaicin-mediated substance P release from cultured rat dorsal root ganglion neurons
- PMID: 22307830
- PMCID: PMC3493032
- DOI: 10.3892/mmr.2012.778
TRESK gene recombinant adenovirus vector inhibits capsaicin-mediated substance P release from cultured rat dorsal root ganglion neurons
Abstract
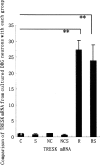
The present study was conducted to determine whether the activation of TRESK in the dorsal root ganglion (DRG) by the TRESK gene recombinant adenovirus vector inhibits the capsaicin-evoked substance P (SP) release using a radioimmunoassay. TRESK is an outwardly rectifying K+ current channel that contributes to the resting potential and is the most important background potassium channel in DRG. Previous studies have shown that neuropathic pain (NP) is closely related to the regulation of certain potassium channels in DRG neurons, while DRG-released SP is important in the peripheral mechanism of NP. In the present study, the TRESK gene adenovirus vector significantly enhanced the TRESK mRNA and protein of the cultured rat DRG neurons. Radioimmunoassay analysis revealed that the capsaicin‑mediated SP release was significantly inhibited by the TRESK gene recombinant adenovirus vector in rat DRG neurons. These findings suggest that TRESK plays a role in adjusting the release of SP in DRG, which is related to NP.
Figures


References
-
- Kang D, Mariash E, Kim D. Functional expression of TRESK-2, a new member of the tandem-pore K+ channel family. J Biol Chem. 2004;279:28063–28070. - PubMed
-
- Kang D, Kim D. TREK-2(K2P 10.1) and TRESK(K2P 18.1) are major background K+ channels in dorsal root ganglion neurons. Am J Physiol Cell Physiol. 2006;291:138–146. - PubMed
-
- Liu C, Au JD, Zou HL, Cotten JF, Yost CS. Potent activation of the human tandem pore domain K channel TRESK with clinical concentrations of volatile anesthetics. Anesth Analg. 2004;99:1715–1722. - PubMed
-
- Keshavaprasad B, Liu C, Au JD, Kindler CH, Cotten JF, Yost CS. Species-specific differences in response to anesthetics and other modulators by the K2P channel TRESK. Anesth Analg. 2005;101:1042–1049. - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous

