Mutations in the Arabidopsis homolog of LST8/GβL, a partner of the target of Rapamycin kinase, impair plant growth, flowering, and metabolic adaptation to long days
- PMID: 22307851
- PMCID: PMC3315227
- DOI: 10.1105/tpc.111.091306
Mutations in the Arabidopsis homolog of LST8/GβL, a partner of the target of Rapamycin kinase, impair plant growth, flowering, and metabolic adaptation to long days
Abstract
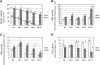
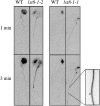
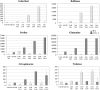
The conserved Target of Rapamycin (TOR) kinase forms high molecular mass complexes and is a major regulator of cellular adaptations to environmental cues. The Lethal with Sec Thirteen 8/G protein β subunit-like (LST8/GβL) protein is a member of the TOR complexes, and two putative LST8 genes are present in Arabidopsis thaliana, of which only one (LST8-1) is significantly expressed. The Arabidopsis LST8-1 protein is able to complement yeast lst8 mutations and interacts with the TOR kinase. Mutations in the LST8-1 gene resulted in reduced vegetative growth and apical dominance with abnormal development of flowers. Mutant plants were also highly sensitive to long days and accumulated, like TOR RNA interference lines, higher amounts of starch and amino acids, including proline and glutamine, while showing reduced concentrations of inositol and raffinose. Accordingly, transcriptomic and enzymatic analyses revealed a higher expression of genes involved in nitrate assimilation when lst8-1 mutants were shifted to long days. The transcriptome of lst8-1 mutants in long days was found to share similarities with that of a myo-inositol 1 phosphate synthase mutant that is also sensitive to the extension of the light period. It thus appears that the LST8-1 protein has an important role in regulating amino acid accumulation and the synthesis of myo-inositol and raffinose during plant adaptation to long days.
Figures





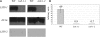





Similar articles
-
Mutations of the AtYAK1 Kinase Suppress TOR Deficiency in Arabidopsis.Cell Rep. 2019 Jun 18;27(12):3696-3708.e5. doi: 10.1016/j.celrep.2019.05.074. Cell Rep. 2019. PMID: 31216485
-
Regulation of plant growth and metabolism by the TOR kinase.Biochem Soc Trans. 2011 Apr;39(2):477-81. doi: 10.1042/BST0390477. Biochem Soc Trans. 2011. PMID: 21428923 Review.
-
Mutations in the Arabidopsis Lst8 and Raptor genes encoding partners of the TOR complex, or inhibition of TOR activity decrease abscisic acid (ABA) synthesis.Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 2015 Nov 27;467(4):992-7. doi: 10.1016/j.bbrc.2015.10.028. Epub 2015 Oct 14. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 2015. PMID: 26459592
-
Overexpression of AtAHL20 causes delayed flowering in Arabidopsis via repression of FT expression.BMC Plant Biol. 2020 Dec 11;20(1):559. doi: 10.1186/s12870-020-02733-5. BMC Plant Biol. 2020. PMID: 33308168 Free PMC article.
-
Shaping plant development through the SnRK1-TOR metabolic regulators.Curr Opin Plant Biol. 2017 Feb;35:152-157. doi: 10.1016/j.pbi.2016.12.004. Epub 2016 Dec 25. Curr Opin Plant Biol. 2017. PMID: 28027512 Review.
Cited by
-
To grow or not to grow under nutrient scarcity: Target of rapamycin-ethylene is the question.Front Plant Sci. 2022 Aug 12;13:968665. doi: 10.3389/fpls.2022.968665. eCollection 2022. Front Plant Sci. 2022. PMID: 36035680 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Role of AGC kinases in plant growth and stress responses.Cell Mol Life Sci. 2012 Oct;69(19):3259-67. doi: 10.1007/s00018-012-1093-3. Epub 2012 Jul 31. Cell Mol Life Sci. 2012. PMID: 22847330 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Regulatory-Associated Protein of TOR 1B (RAPTOR1B) regulates hormonal switches during seed germination in Arabidopsis thaliana.Plant Signal Behav. 2019;14(7):1613130. doi: 10.1080/15592324.2019.1613130. Epub 2019 May 6. Plant Signal Behav. 2019. PMID: 31058576 Free PMC article.
-
The role of target of rapamycin signaling networks in plant growth and metabolism.Plant Physiol. 2014 Feb;164(2):499-512. doi: 10.1104/pp.113.229948. Epub 2014 Jan 2. Plant Physiol. 2014. PMID: 24385567 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Translational gene regulation in plants: A green new deal.Wiley Interdiscip Rev RNA. 2020 Nov;11(6):e1597. doi: 10.1002/wrna.1597. Epub 2020 May 4. Wiley Interdiscip Rev RNA. 2020. PMID: 32367681 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Adami A., García-Alvarez B., Arias-Palomo E., Barford D., Llorca O. (2007). Structure of TOR and its complex with KOG1. Mol. Cell 27: 509–516 - PubMed
-
- Alonso J.M., et al. (2003). Genome-wide insertional mutagenesis of Arabidopsis thaliana. Science 301: 653–657 - PubMed
-
- Bernier G., Périlleux C. (2005). A physiological overview of the genetics of flowering time control. Plant Biotechnol. J. 3: 3–16 - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Associated data
- Actions
- Actions

