Structural dynamics of bacterial translation initiation factor IF2
- PMID: 22308033
- PMCID: PMC3322840
- DOI: 10.1074/jbc.M111.333393
Structural dynamics of bacterial translation initiation factor IF2
Abstract
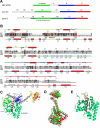
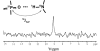
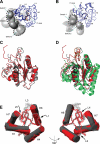
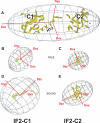
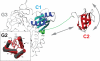
Bacterial translation initiation factor IF2 promotes ribosomal subunit association, recruitment, and binding of fMet-tRNA to the ribosomal P-site and initiation dipeptide formation. Here, we present the solution structures of GDP-bound and apo-IF2-G2 of Bacillus stearothermophilus and provide evidence that this isolated domain binds the 50 S ribosomal subunit and hydrolyzes GTP. Differences between the free and GDP-bound structures of IF2-G2 suggest that domain reorganization within the G2-G3-C1 regions underlies the different structural requirements of IF2 during the initiation process. However, these structural signals are unlikely forwarded from IF2-G2 to the C-terminal fMet-tRNA binding domain (IF2-C2) because the connected IF2-C1 and IF2-C2 modules show completely independent mobility, indicating that the bacterial interdomain connector lacks the rigidity that was found in the archaeal IF2 homolog aIF5B.
Figures
References
-
- Boelens R., Gualerzi C. O. (2002) Structure and function of bacterial initiation factors. Curr. Protein Pept. Sci. 3, 107–119 - PubMed
-
- Gualerzi C. O., Fabbretti A., Brandi L., Milon P., Pon C. L. (2010) Role of the initiation factors in mRNA start site selection and fMet-tRNA recruitment by bacterial ribosomes. Isr. J. Chem. 50, 80–94
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Associated data
- Actions
- Actions
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous

