Drosophila Dopamine2-like receptors function as autoreceptors
- PMID: 22308204
- PMCID: PMC3269839
- DOI: 10.1021/cn200057k
Drosophila Dopamine2-like receptors function as autoreceptors
Abstract
Dopaminergic signaling pathways are conserved between mammals and Drosophila and D2 receptors have been identified in Drosophila. However, it has not been demonstrated whether Drosophila D2 receptors function as autoreceptors and regulate the release of dopamine. The goal of this study was to determine if Drosophila D2 receptors act as autoreceptors by probing the extent to which D2 agonists and antagonists affect evoked dopamine release. Fast-scan cyclic voltammetry was used to measure stimulated dopamine release at a carbon-fiber microelectrode implanted in an intact, larval Drosophila nervous system. Dopamine release was evoked using 5-second blue light stimulations that open Channelrhodopsin-2, a blue light activated cation channel that was specifically expressed in dopaminergic neurons. In mammals, administration of a D2 agonist decreases evoked dopamine release by increasing autoreceptor feedback. Similarly, we found that the D2 agonists bromocriptine and quinpirole decreased stimulated dopamine release in Drosophila. D2 antagonists were expected to increase dopamine release and the D2 antagonists flupenthixol, butaclamol, and haloperidol did increase stimulated release. Agonists did not significantly modulate dopamine uptake although the modulatory effects of D2 drugs on release were affected by prior administration of the uptake inhibitor nisoxetine. These results demonstrate that the D2 receptor functions as an autoreceptor in Drosophila. The similarities in dopamine regulation validate Drosophila as a model system for studying the basic neurobiology of dopaminergic signaling.
Figures
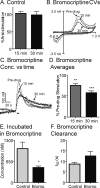

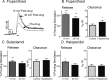
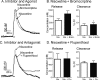
References
-
- Neve K. A. (2004) Dopamine Receptors. In Encyclopedia of Biological Chemistry, pp 817–22, Elsevier, New York.
-
- Creese I.; Burt D. R.; Snyder S. H. (1976) Dopamine receptor binding predicts clinical and pharmacological potencies of antischizophrenic drugs. Science 192, 481–3. - PubMed
-
- Gurevich E. V., and Gurevich V. V. (2010) Dopamine Receptors and the Treatment of Parkinson’s Disease. In The Dopamine Receptors, pp 525–84, Humana Press, Totowa, NJ.
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases

