Derivation and maintenance of virtual memory CD8 T cells
- PMID: 22308307
- PMCID: PMC3294185
- DOI: 10.4049/jimmunol.1102213
Derivation and maintenance of virtual memory CD8 T cells
Erratum in
- J Immunol. 2014 Sep 1;193(5):2609
Abstract
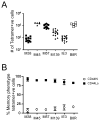
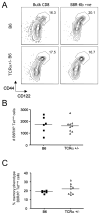
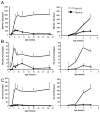
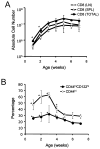
Memory CD8(+) T cells are an important component of the adaptive immune response against many infections, and understanding how Ag-specific memory CD8(+) T cells are generated and maintained is crucial for the development of vaccines. We recently reported the existence of memory-phenotype, Ag-specific CD8(+) T cells in unimmunized mice (virtual memory or VM cells). However, it was not clear when and where these cells are generated during normal development, nor the factors required for their production and maintenance. This issue is especially pertinent given recent data showing that memory-like CD8 T cells can be generated in the thymus, in a bystander response to IL-4. In this study, we show that the size of the VM population is reduced in IL-4R-deficient animals. However, the VM population appears first in the periphery and not the thymus of normal animals, suggesting this role of IL-4 is manifest following thymic egress. We also show that the VM pool is durable, showing basal proliferation and long-term maintenance in normal animals, and also being retained during responses to unrelated infection.
Figures



References
-
- Badovinac VP, Harty JT. CD8(+) T-cell homeostasis after infection: setting the ‘curve’. Microbes and infection/Institut Pasteur. 2002;4:441–447. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials

