Withania somnifera reverses Alzheimer's disease pathology by enhancing low-density lipoprotein receptor-related protein in liver
- PMID: 22308347
- PMCID: PMC3295277
- DOI: 10.1073/pnas.1112209109
Withania somnifera reverses Alzheimer's disease pathology by enhancing low-density lipoprotein receptor-related protein in liver
Abstract
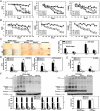
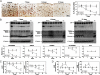
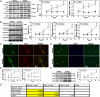
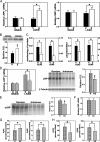
A 30-d course of oral administration of a semipurified extract of the root of Withania somnifera consisting predominantly of withanolides and withanosides reversed behavioral deficits, plaque pathology, accumulation of β-amyloid peptides (Aβ) and oligomers in the brains of middle-aged and old APP/PS1 Alzheimer's disease transgenic mice. It was similarly effective in reversing behavioral deficits and plaque load in APPSwInd mice (line J20). The temporal sequence involved an increase in plasma Aβ and a decrease in brain Aβ monomer after 7 d, indicating increased transport of Aβ from the brain to the periphery. Enhanced expression of low-density lipoprotein receptor-related protein (LRP) in brain microvessels and the Aβ-degrading protease neprilysin (NEP) occurred 14-21 d after a substantial decrease in brain Aβ levels. However, significant increase in liver LRP and NEP occurred much earlier, at 7 d, and were accompanied by a rise in plasma sLRP, a peripheral sink for brain Aβ. In WT mice, the extract induced liver, but not brain, LRP and NEP and decreased plasma and brain Aβ, indicating that increase in liver LRP and sLRP occurring independent of Aβ concentration could result in clearance of Aβ. Selective down-regulation of liver LRP, but not NEP, abrogated the therapeutic effects of the extract. The remarkable therapeutic effect of W. somnifera mediated through up-regulation of liver LRP indicates that targeting the periphery offers a unique mechanism for Aβ clearance and reverses the behavioral deficits and pathology seen in Alzheimer's disease models.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures
Comment in
-
Extracting β-amyloid from Alzheimer's disease.Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2012 Feb 28;109(9):3199-200. doi: 10.1073/pnas.1121560109. Epub 2012 Feb 10. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2012. PMID: 22328154 Free PMC article. No abstract available.
References
-
- Hardy J. A hundred years of Alzheimer's disease research. Neuron. 2006;52:3–13. - PubMed
-
- Citron M. Strategies for disease modification in Alzheimer's disease. Nat Rev Neurosci. 2004;5:677–685. - PubMed
-
- Citron M. Alzheimer's disease: Strategies for disease modification. Nat Rev Drug Discov. 2010;9:387–398. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Molecular Biology Databases
Miscellaneous

