Host-targeting protein 1 (SpHtp1) from the oomycete Saprolegnia parasitica translocates specifically into fish cells in a tyrosine-O-sulphate-dependent manner
- PMID: 22308362
- PMCID: PMC3277526
- DOI: 10.1073/pnas.1113775109
Host-targeting protein 1 (SpHtp1) from the oomycete Saprolegnia parasitica translocates specifically into fish cells in a tyrosine-O-sulphate-dependent manner
Abstract
The eukaryotic oomycetes, or water molds, contain several species that are devastating pathogens of plants and animals. During infection, oomycetes translocate effector proteins into host cells, where they interfere with host-defense responses. For several oomycete effectors (i.e., the RxLR-effectors) it has been shown that their N-terminal polypeptides are important for the delivery into the host. Here we demonstrate that the putative RxLR-like effector, host-targeting protein 1 (SpHtp1), from the fish pathogen Saprolegnia parasitica translocates specifically inside host cells. We further demonstrate that cell-surface binding and uptake of this effector protein is mediated by an interaction with tyrosine-O-sulfate-modified cell-surface molecules and not via phospholipids, as has been reported for RxLR-effectors from plant pathogenic oomycetes. These results reveal an effector translocation route based on tyrosine-O-sulfate binding, which could be highly relevant for a wide range of host-microbe interactions.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures
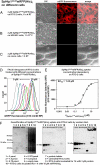
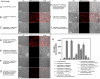
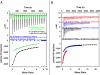
References
-
- Birch PR, et al. Towards understanding the virulence functions of RXLR effectors of the oomycete plant pathogen Phytophthora infestans. J Exp Bot. 2009;60:1133–1140. - PubMed
-
- Mattoo S, Lee YM, Dixon JE. Interactions of bacterial effector proteins with host proteins. Curr Opin Immunol. 2007;19:392–401. - PubMed
-
- Stergiopoulos I, de Wit PJ. Fungal effector proteins. Annu Rev Phytopathol. 2009;47:233–263. - PubMed
-
- Salmond GP, Reeves PJ. Membrane traffic wardens and protein secretion in gram-negative bacteria. Trends Biochem Sci. 1993;18:7–12. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials

