High-resolution structure of a BRICHOS domain and its implications for anti-amyloid chaperone activity on lung surfactant protein C
- PMID: 22308375
- PMCID: PMC3289314
- DOI: 10.1073/pnas.1114740109
High-resolution structure of a BRICHOS domain and its implications for anti-amyloid chaperone activity on lung surfactant protein C
Abstract
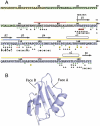
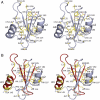
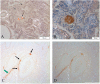
BRICHOS domains are encoded in > 30 human genes, which are associated with cancer, neurodegeneration, and interstitial lung disease (ILD). The BRICHOS domain from lung surfactant protein C proprotein (proSP-C) is required for membrane insertion of SP-C and has anti-amyloid activity in vitro. Here, we report the 2.1 Å crystal structure of the human proSP-C BRICHOS domain, which, together with molecular dynamics simulations and hydrogen-deuterium exchange mass spectrometry, reveals how BRICHOS domains may mediate chaperone activity. Observation of amyloid deposits composed of mature SP-C in lung tissue samples from ILD patients with mutations in the BRICHOS domain or in its peptide-binding linker region supports the in vivo relevance of the proposed mechanism. The results indicate that ILD mutations interfering with proSP-C BRICHOS activity cause amyloid disease secondary to intramolecular chaperone malfunction.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures
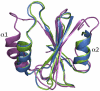

References
-
- Mulugeta S, Beers MF. Surfactant protein C: its unique properties and emerging immunomodulatory role in the lung. Microbes Infect. 2006;8:2317–2323. - PubMed
-
- Beers MF, Kim CY, Dodia C, Fisher AB. Localization, synthesis, and processing of surfactant protein SP-C in rat lung analyzed by epitope-specific antipeptide antibodies. J Biol Chem. 1994;269:20318–20328. - PubMed
-
- Johansson J, Szyperski T, Curstedt T, Wüthrich K. The NMR structure of the pulmonary surfactant-associated polypeptide SP-C in an apolar solvent contains a valyl-rich α-helix. Biochemistry. 1994;33:6015–6023. - PubMed
-
- Mingarro I, Nilsson I, Whitley P, von Heijne G. Different conformations of nascent polypeptides during translocation across the ER membrane. BMC Cell Biol. 2000;1 Available at http://www.biomedcentral.com/1471-2121/1/3. - PMC - PubMed
-
- Kallberg Y, Gustafsson M, Persson B, Thyberg J, Johansson J. Prediction of amyloid fibril-forming proteins. J Biol Chem. 2001;276:12945–12950. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Associated data
- Actions
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases

