CD4 and CD8 T cells require different membrane gangliosides for activation
- PMID: 22308377
- PMCID: PMC3277553
- DOI: 10.1073/pnas.1114965109
CD4 and CD8 T cells require different membrane gangliosides for activation
Abstract
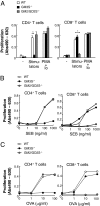
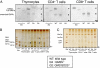
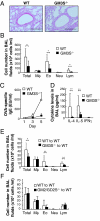
Initial events of T-cell activation involve movement of the T-cell receptor into lipid rafts. Gangliosides are major components of lipid rafts. While investigating T-cell activation in ganglioside-deficient mice, we observed that CD4(+) and CD8(+) T cells required different ganglioside subsets for activation. Activation of CD4(+) T cells from GM3 synthase-null mice, deficient in GM3-derived gangliosides, is severely compromised, whereas CD8(+) T-cell activation is normal. Conversely, in cells from GM2/GD2 synthase-null mice, expressing only GM3 and GD3, CD4(+) T-cell activation is normal, whereas CD8(+) T-cell activation is deficient. Supplementing the cells with the corresponding missing gangliosides restores normal activation. GM3 synthase-null mice do not develop experimental asthma. Distinct expression patterns of ganglioside species in CD4(+) T and CD8(+) T cells, perhaps in uniquely functional lipid rafts, define immune functions in each T-cell subset. Control of ganglioside expression would offer a strategy targeting for specific T-cell subpopulations to treat immune diseases.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures



References
-
- Simons K, Ikonen E. Functional rafts in cell membranes. Nature. 1997;387:569–572. - PubMed
-
- Dykstra M, Cherukuri A, Sohn HW, Tzeng SJ, Pierce SK. Location is everything: Lipid rafts and immune cell signaling. Annu Rev Immunol. 2003;21:457–481. - PubMed
-
- Harder T, Rentero C, Zech T, Gaus K. Plasma membrane segregation during T cell activation: Probing the order of domains. Curr Opin Immunol. 2007;19:470–475. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials

