Chondroitinase ABC promotes selective reactivation of somatosensory cortex in squirrel monkeys after a cervical dorsal column lesion
- PMID: 22308497
- PMCID: PMC3289303
- DOI: 10.1073/pnas.1121604109
Chondroitinase ABC promotes selective reactivation of somatosensory cortex in squirrel monkeys after a cervical dorsal column lesion
Abstract
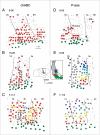
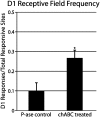
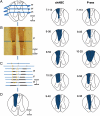
After large but incomplete lesions of ascending dorsal column afferents in the cervical spinal cord, the hand representation in the contralateral primary somatosensory cortex (area 3b) of monkeys is largely or completely unresponsive to touch on the hand. However, after weeks of spontaneous recovery, considerable reactivation of the hand territory in area 3b can occur. Because the reactivation process likely depends on the sprouting of remaining axons from the hand in the cuneate nucleus of the lower brainstem, we sought to influence cortical reactivation by treating the cuneate nucleus with an enzyme, chondroitinase ABC, that digests perineuronal nets, promoting axon sprouting. Dorsal column lesions were placed at a spinal cord level (C5/C6) that allowed a portion of ascending afferents from digit 1 to survive in squirrel monkeys. After 11-12 wk of recovery, the contralateral forelimb cortex was reactivated by stimulating digit 1 more extensively in treated monkeys than in control monkeys. The results are consistent with the proposal that the treatment enhances the sprouting of digit 1 afferents in the cuneate nucleus and that this sprouting allowed these preserved inputs to activate cortex more effectively.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures
References
-
- Merzenich MM, et al. Progression of change following median nerve section in the cortical representation of the hand in areas 3b and 1 in adult owl and squirrel monkeys. Neuroscience. 1983;10:639–665. - PubMed
-
- Jain N, Catania KC, Kaas JH. Deactivation and reactivation of somatosensory cortex after dorsal spinal cord injury. Nature. 1997;386:495–498. - PubMed
-
- Darian-Smith C, Brown S. Functional changes at periphery and cortex following dorsal root lesions in adult monkeys. Nat Neurosci. 2000;3:476–481. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous

