The effects of varying alcohol concentrations commonly found in mouth rinses on the force decay of elastomeric chain
- PMID: 22309124
- PMCID: PMC8823131
- DOI: 10.2319/062211-407.1
The effects of varying alcohol concentrations commonly found in mouth rinses on the force decay of elastomeric chain
Abstract
Objective: To test the effect of alcohol on force decay of elastomeric chains in vitro in order to determine if increasing alcohol concentrations results in an increased amount of elastomeric chain force decay.
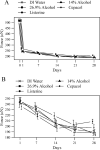
Materials and methods: A prospective laboratory study was completed to test the effect of alcohol exposure on orthodontic elastomeric chain. A total of 450 specimens were divided into five test groups. Two test groups were each exposed to different alcohol concentrations (14% and 26.9%) and the other two test groups were exposed to different commercially available mouth rinses (Cēpacol -14% alcohol and Listerine - 26.9% alcohol) for 60 seconds twice a day. The control group followed all of the same procedures but was only exposed to deionized (DI) water. Force measurements were taken at six time points (initial, 1 day, 7 days, 14 days, 21 days, and 28 days).
Results: There were no significant differences among groups at the initial time point (P = .52). Statistically significant effects of time on force decay were seen in all groups. All test groups showed significantly more force decay than the control group. Only a few statistically significant differences were observed when comparing force decay among the test groups.
Conclusions: Alcohol causes an increase in force decay of elastomeric chain over time. A concentration dependence of alcohol on force decay of elastomeric chain was not observed.
Figures

References
-
- Ash J. L, Nikolai R. J. Relaxation of orthodontic elastomeric chains and modules in vitro and in vivo. J Dent Res. 1978;57:685–690. - PubMed
-
- De Genova D. C, McInnes-Ledoux P, Weinberg R, Shaye R. Force degradation of orthodontic elastomeric chains—a product comparison study. Am J Orthod. 1985;87:377–384. - PubMed
-
- Eliades T, Eliades G, Silikas N, Watts D. C. In vitro degradation of polyurethane orthodontic elastomeric modules. J Oral Rehabil. 2005;32:72–77. - PubMed
-
- Ferriter J. P, Meyers C. E, Jr, Lorton L. The effect of hydrogen ion concentration on the force-degradation rate of orthodontic polyurethane chain elastics. Am J Orthod Dentofacial Orthop. 1990;98:404–410. - PubMed
-
- Kuster R, Ingervall B, Burgin W. Laboratory and intra-oral tests of the degradation of elastic chains. Eur J Orthod. 1986;8:202–208. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

