Mechanism and specificity of the human paracaspase MALT1
- PMID: 22309193
- PMCID: PMC3304489
- DOI: 10.1042/BJ20120035
Mechanism and specificity of the human paracaspase MALT1
Abstract
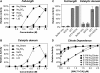
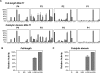
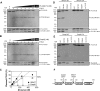
The paracaspase domain of MALT1 (mucosa-associated lymphoid tissue lymphoma translocation protein 1) is a component of a gene translocation fused to the N-terminal domains of the cellular inhibitor of apoptosis protein 2. The paracaspase itself, commonly known as MALT1, participates in the NF-κB (nuclear factor κB) pathway, probably by driving survival signals downstream of the B-cell antigen receptor through MALT1 proteolytic activity. We have developed methods for the expression and purification of recombinant full-length MALT1 and its constituent catalytic domain alone. Both are activated by dimerization without cleavage, with a similar dimerization barrier to the distantly related cousins, the apical caspases. By using positional-scanning peptidyl substrate libraries we demonstrate that the activity and specificity of full-length MALT1 is recapitulated by the catalytic domain alone, showing a stringent requirement for cleaving after arginine, and with striking peptide length constraints for efficient hydrolysis. Rates of cleavage (kcat/Km values) of optimal peptidyl substrates are in the same order (10(3)-10(4) M(-1)·s(-1)) as for a putative target protein CYLD. Thus MALT1 has many similarities to caspase 8, even cleaving the putative target protein CYLD with comparable efficiencies, but with diametrically opposite primary substrate specificity.
Figures


References
-
- Dierlamm J., Baens M., Wlodarska I., Stefanova-Ouzounova M., Hernandez J. M., Hossfeld D. K., De Wolf-Peeters C., Hagemeijer A., Van den Berghe H., Marynen P. The apoptosis inhibitor gene API2 and a novel 18q gene, MLT, are recurrently rearranged in the t(11;18)(q21;q21) associated with mucosa-associated lymphoid tissue lymphomas. Blood. 1999;93:3601–3609. - PubMed
-
- Uren A. G., O'Rourke K., Aravind L. A., Pisabarro M. T., Seshagiri S., Koonin E. V., Dixit V. M. Identification of paracaspases and metacaspases: two ancient families of caspase-like proteins, one of which plays a key role in MALT lymphoma. Mol. Cell. 2000;6:961–967. - PubMed
-
- Gaide O., Favier B., Legler D. F., Bonnet D., Brissoni B., Valitutti S., Bron C., Tschopp J., Thome M. CARMA1 is a critical lipid raft-associated regulator of TCR-induced NF-κB activation. Nat. Immunol. 2002;3:836–843. - PubMed
-
- Wang D., You Y., Case S. M., McAllister-Lucas L. M., Wang L., DiStefano P. S., Nunez G., Bertin J., Lin X. A requirement for CARMA1 in TCR-induced NF-κB activation. Nat. Immunol. 2002;3:830–835. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials

