Sensitive and rapid quantification of C-reactive protein using quantum dot-labeled microplate immunoassay
- PMID: 22309411
- PMCID: PMC3295717
- DOI: 10.1186/1479-5876-10-24
Sensitive and rapid quantification of C-reactive protein using quantum dot-labeled microplate immunoassay
Abstract
Background: High-sensitivity C-reactive protein (hs-CRP) assay is of great clinical importance in predicting risks associated with coronary heart disease. Existing hs-CRP assays either require complex operation or have low throughput and cannot be routinely implemented in rural settings due to limited laboratory resources.
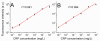
Methods: We developed a novel hs-CRP assay capable of simultaneously quantifying over 90 clinical samples by using quantum dots-labeled immunoassay within a standard 96-well microplate. The specificity of the assay was enhanced by adopting two monoclonal antibodies (mAbs) that target distinct hs-CRP epitopes, serving as the coating antibody and the detection antibody, respectively. In the presence of hs-CRP antigen, the fluorescence intensity of the mAb-Ag-mAb sandwich complex captured on the microplate can be read out using a microplate reader.
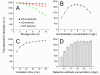
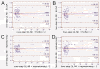
Results: The proposed hs-CRP assay provides a wide analytical range of 0.001-100 mg/L with a detection limit of 0.06 (0.19) μg/L within 1.5 h. The accuracy of the proposed assay has been confirmed for low coefficient of variations (CVs), 2.27% (intra-assay) and 8.52% (inter-assay), together with recoveries of 96.7-104.2%. Bland-Altman plots of 104 clinical samples exhibited good consistency among the proposed assay, commercial high-sensitivity ELISA, and nephelometry, indicating the prospects of the newly developed hs-CRP assay as an alternative to existing hs-CRP assays.
Conclusion: The developed assay meets the needs of the rapid, sensitive and high-throughput determination of hs-CRP levels within a short time using minimal resources. In addition, the developed assay can also be used to detect and quantify other diagnostic biomarkers by immobilizing specific monoclonal antibodies.
Figures


References
-
- Sabatine MS, Morrow DA, de Lemos JA, Gibson CM, Murphy SA, Rifai N, McCabe C, Antman EM, Cannon CP, Braunwald E. Multimarker approach to risk stratification in non-ST elevation acute coronary syndromes: simultaneous assessment of troponin I, C-reactive protein, and B-type natriuretic peptide. Circulation. 2002;105:1760–1763. - PubMed
-
- Danesh J, Wheeler JG, Hirschfield GM, Eda S, Eiriksdottir G, Rumley A, Lowe GD, Pepys MB, Gudnason V. C-reactive protein and other circulating markers of inflammation in the prediction of coronary heart disease. N Engl J Med. 2004;350:1387–1397. - PubMed
-
- Ridker PM, Hennekens CH, Buring JE, Rifai N. C-reactive protein and other markers of inflammation in the prediction of cardiovascular disease in women. N Engl J Med. 2000;342:836–843. - PubMed
-
- Pradhan AD, Manson JE, Rifai N, Buring JE, Ridker PM. C-reactive protein, interleukin 6, and risk of developing type 2 diabetes mellitus. JAMA. 2001;286:327–334. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

