Comparison of the performance of DBA/2 and C57BL/6 mice in transitive inference and foreground and background contextual fear conditioning
- PMID: 22309443
- PMCID: PMC3314134
- DOI: 10.1037/a0027048
Comparison of the performance of DBA/2 and C57BL/6 mice in transitive inference and foreground and background contextual fear conditioning
Abstract
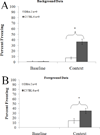
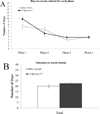
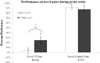
DBA/2 mice have altered hippocampal structure and perform poorly in several hippocampus-dependent contextual/spatial learning tasks. The performance of this strain in higher cognitive tasks is less studied. Transitive inference is a hippocampus-dependent task that requires an abstraction to be made from prior rules to form a new decision matrix; performance of DBA/2 mice in this task is unknown, whereas contextual fear conditioning is a hippocampus-dependent task in which DBA/2 mice have deficits. The present study compared DBA/2J and C57BL/6J inbred mice in two different contextual fear conditioning paradigms and transitive inference to test whether similar deficits are seen across these hippocampus-dependent tasks. For background fear conditioning, mice were trained with two paired presentations of an auditory conditioned stimulus (CS, 30 seconds, 85 dB white noise) paired with an unconditioned stimulus (US, 2 seconds, 0.57 mA footshock), the context was a continuous background CS. Mice were tested for contextual learning 24 hours later. Foreground fear conditioning differed in that no auditory CS was presented. For transitive inference, separate mice were trained to acquire a series of overlapping odor discrimination problems and tested with novel odor pairings that either did or did not require the use of transitive inference. DBA/2 mice performed significantly worse than the C57BL/6 in both foreground and background fear conditioning and transitive inference. These results demonstrate that the DBA/2 mice have deficits in higher-cognitive processes and suggest that similar substrates may underlie deficits in contextual learning and transitive inference.
(c) 2012 APA, all rights reserved
Figures
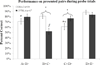
Similar articles
-
DBA/2 and C57BL/6 mice differ in contextual fear but not auditory fear conditioning.Behav Neurosci. 1994 Aug;108(4):810-7. doi: 10.1037//0735-7044.108.4.810. Behav Neurosci. 1994. PMID: 7986374
-
Fear conditioning in C57/BL/6 and DBA/2 mice: variability in nucleus accumbens function according to the strain predisposition to show contextual- or cue-based responding.Eur J Neurosci. 2000 Dec;12(12):4467-74. Eur J Neurosci. 2000. PMID: 11122357
-
Nicotine enhances both foreground and background contextual fear conditioning.Neurosci Lett. 2006 Feb 20;394(3):202-5. doi: 10.1016/j.neulet.2005.10.026. Epub 2005 Nov 2. Neurosci Lett. 2006. PMID: 16260086 Free PMC article.
-
Is the hippocampus necessary for contextual fear conditioning?Behav Brain Res. 2000 Jun 1;110(1-2):83-95. doi: 10.1016/s0166-4328(99)00187-4. Behav Brain Res. 2000. PMID: 10802306 Review.
-
Contextual inference in learning and memory.Trends Cogn Sci. 2023 Jan;27(1):43-64. doi: 10.1016/j.tics.2022.10.004. Epub 2022 Nov 24. Trends Cogn Sci. 2023. PMID: 36435674 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Mutations in neuroligin-3 in male mice impact behavioral flexibility but not relational memory in a touchscreen test of visual transitive inference.Mol Autism. 2019 Dec 2;10:42. doi: 10.1186/s13229-019-0292-2. eCollection 2019. Mol Autism. 2019. PMID: 31827744 Free PMC article.
-
Discovering Implied Serial Order Through Model-Free and Model-Based Learning.Front Neurosci. 2019 Aug 20;13:878. doi: 10.3389/fnins.2019.00878. eCollection 2019. Front Neurosci. 2019. PMID: 31481871 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Behavioral tests assessing neuropsychiatric phenotypes in adolescent mice reveal strain- and sex-specific effects.Sci Rep. 2020 Jul 9;10(1):11263. doi: 10.1038/s41598-020-67758-0. Sci Rep. 2020. PMID: 32647155 Free PMC article.
-
Longitudinal analysis of ultrasonic vocalizations in mice from infancy to adolescence: Insights into the vocal repertoire of three wild-type strains in two different social contexts.PLoS One. 2019 Jul 31;14(7):e0220238. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0220238. eCollection 2019. PLoS One. 2019. PMID: 31365551 Free PMC article.
-
Cognitive abilities on transitive inference using a novel touchscreen technology for mice.Cereb Cortex. 2015 May;25(5):1133-42. doi: 10.1093/cercor/bht293. Epub 2013 Nov 28. Cereb Cortex. 2015. PMID: 24293564 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Ammassari-Teule, Passino E, Restivo L, de Marsanich B. Fear conditioning in c57/bl/6 and dba/2 mice: Variability in nucleus accumbens function according to the strain predisposition to show contextual- or cue-based responding. The European journal of neuroscience. 2000;12(12):4467–4474. - PubMed
-
- Ammassari-Teule, Tozzi A, Rossi-Arnaud C, Save E, Thinus-Blanc C. Reactions to spatial and nonspatial change in two inbred strains of mice: Further evidence supporting the hippocampal dysfunction hypothesis in the dba:2 strain. Psychobiology. 1995;23:284–289.
-
- Anagnostaras SG, Gale GD, Fanselow MS. Hippocampus and contextual fear conditioning: Recent controversies and advances. Hippocampus. 2001;11(1):8–17. - PubMed
-
- Bailey A, Metaxas A, Al-Hasani R, Keyworth HL, Forster DM, Kitchen I. Mouse strain differences in locomotor, sensitisation and rewarding effect of heroin; association with alterations in mop-r activation and dopamine transporter binding. The European journal of neuroscience. 2010;31(4):742–753. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous

