Quality assessment of expert answers to lay questions about cystic fibrosis from various language zones in Europe: the ECORN-CF project
- PMID: 22309508
- PMCID: PMC3311602
- DOI: 10.1186/1471-2288-12-11
Quality assessment of expert answers to lay questions about cystic fibrosis from various language zones in Europe: the ECORN-CF project
Abstract
Background: The European Centres of Reference Network for Cystic Fibrosis (ECORN-CF) established an Internet forum which provides the opportunity for CF patients and other interested people to ask experts questions about CF in their mother language. The objectives of this study were to: 1) develop a detailed quality assessment tool to analyze quality of expert answers, 2) evaluate the intra- and inter-rater agreement of this tool, and 3) explore changes in the quality of expert answers over the time frame of the project.
Methods: The quality assessment tool was developed by an expert panel. Five experts within the ECORN-CF project used the quality assessment tool to analyze the quality of 108 expert answers published on ECORN-CF from six language zones. 25 expert answers were scored at two time points, one year apart. Quality of answers was also assessed at an early and later period of the project. Individual rater scores and group mean scores were analyzed for each expert answer.
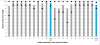
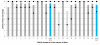
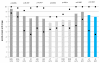
Results: A scoring system and training manual were developed analyzing two quality categories of answers: content and formal quality. For content quality, the grades based on group mean scores for all raters showed substantial agreement between two time points, however this was not the case for the grades based on individual rater scores. For formal quality the grades based on group mean scores showed only slight agreement between two time points and there was also poor agreement between time points for the individual grades. The inter-rater agreement for content quality was fair (mean kappa value 0.232 ± 0.036, p < 0.001) while only slight agreement was observed for the grades of the formal quality (mean kappa value 0.105 ± 0.024, p < 0.001). The quality of expert answers was rated high (four language zones) or satisfactory (two language zones) and did not change over time.
Conclusions: The quality assessment tool described in this study was feasible and reliable when content quality was assessed by a group of raters. Within ECORN-CF, the tool will help ensure that CF patients all over Europe have equal possibility of access to high quality expert advice on their illness.
© 2012 d’Alquen et al; licensee BioMed Central Ltd.
Figures

References
-
- Santis G. In: Cystic fibrosis. 2. Hodson ME, Geddes D, editor. London, Arnold; 2000. Basic molecular biology.
-
- Lewis PA. In: Cystic fibrosis. 2. Hodson ME, Geddes D, editor. London, Arnold; 2000. The epidemiology of cystic fibrosis.
-
- Statistics Division, UN Department of Economic and Social Affairs. Statistical yearbook. 52. New York, NY, United Nations; 2008. Gross domestic product and gross domestic product per capita; pp. 171–188.
Publication types
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Molecular Biology Databases

