Identification of NIPSNAP1 as a nocistatin-interacting protein involving pain transmission
- PMID: 22311985
- PMCID: PMC3322983
- DOI: 10.1074/jbc.M111.271866
Identification of NIPSNAP1 as a nocistatin-interacting protein involving pain transmission
Abstract
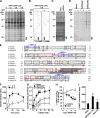
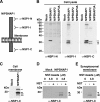
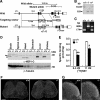
4-Nitrophenylphosphatase domain and non-neuronal SNAP25-like protein homolog 1 (NIPSNAP1) is a molecule of physiologically unknown function, although it is predominantly expressed in the brain, spinal cord, liver, and kidney. We identified NIPSNAP1 as a protein that interacts with the neuropeptide nocistatin (NST) from synaptosomal membranes of mouse spinal cord using high-performance affinity latex beads. NST, which is produced from the same precursor protein as an opioid-like neuropeptide nociceptin/orphanin FQ (N/OFQ), has opposite effects on pain transmission evoked by N/OFQ. The calculated full-length pre-protein of NIPSNAP1 was 33 kDa, whereas the N-terminal truncated form of NIPSNAP1 (29 kDa) was ubiquitously expressed in the neuronal tissues, especially in synaptic membrane and mitochondria of brain. The 29-kDa NIPSNAP1 was distributed on the cell surface, and NST interacted with the 29-kDa but not the 33-kDa NIPSNAP1. Although intrathecal injection of N/OFQ induced tactile allodynia in both wild-type and NIPSNAP1-deficient mice, the inhibition of N/OFQ-evoked tactile allodynia by NST seen in wild-type mice was completely lacking in the deficient mice. These results suggest that NIPSNAP1 is an interacting molecule of NST and plays a crucial role in pain transmission.
Figures



References
-
- Seroussi E., Pan H. Q., Kedra D., Roe B. A., Dumanski J. P. (1998) Characterization of the human NIPSNAP1 gene from 22q12. A member of a novel gene family. Gene. 212, 13–20 - PubMed
-
- Satoh K., Takeuchi M., Oda Y., Deguchi-Tawarada M., Sakamoto Y., Matsubara K., Nagasu T., Takai Y. (2002) Identification of activity-regulated proteins in the postsynaptic density fraction. Genes Cells 7, 187–197 - PubMed
-
- Surendran S., Tyring S. K., Matalon R. (2005) Expression of calpastatin, minopontin, NIPSNAP1, rabaptin-5 and neuronatin in the phenylketonuria (PKU) mouse brain. Possible role on cognitive defect seen in PKU. Neurochem. Int. 46, 595–599 - PubMed
-
- Tummala H., Li X., Homayouni R. (2010) Interaction of a novel mitochondrial protein, 4-nitrophenylphosphatase domain and non-neuronal SNAP25-like protein homolog 1 (NIPSNAP1), with the amyloid precursor protein family. Eur. J. Neurosci. 31, 1926–1934 - PubMed
-
- Nautiyal M., Sweatt A. J., MacKenzie J. A., Mark Payne R., Szucs S., Matalon R., Wallin R., Hutson S. M. (2010) Neuronal localization of the mitochondrial protein NIPSNAP1 in rat nervous system. Eur. J. Neurosci. 32, 560–569 - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Molecular Biology Databases

