The 2'-O-methylation status of a single guanosine controls transfer RNA-mediated Toll-like receptor 7 activation or inhibition
- PMID: 22312111
- PMCID: PMC3280869
- DOI: 10.1084/jem.20111075
The 2'-O-methylation status of a single guanosine controls transfer RNA-mediated Toll-like receptor 7 activation or inhibition
Abstract
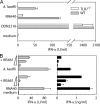
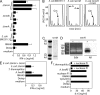
Foreign RNA serves as pathogen-associated molecular pattern (PAMP) and is a potent immune stimulator for innate immune receptors. However, the role of single bacterial RNA species in immune activation has not been characterized in detail. We analyzed the immunostimulatory potential of transfer RNA (tRNA) from different bacteria. Interestingly, bacterial tRNA induced type I interferon (IFN) and inflammatory cytokines in mouse dendritic cells (DCs) and human peripheral blood mononuclear cells (PBMCs). Cytokine production was TLR7 dependent because TLR7-deficient mouse DCs did not respond and TLR7 inhibitory oligonucleotides inhibited tRNA-mediated activation. However, not all bacterial tRNA induced IFN-α because tRNA from Escherichia coli Nissle 1917 and Thermus thermophilus were non-immunostimulatory. Of note, tRNA from an E. coli knockout strain for tRNA (Gm18)-2'-O-methyltransferase (trmH) regained immunostimulatory potential. Additionally, in vitro methylation of this immunostimulatory Gm18-negative tRNA with recombinant trmH from T. thermophilus abolished its IFN-α inducing potential. More importantly, Gm18-modified tRNA acted as TLR7 antagonist and blocked IFN-α induction of influenza A virus-infected PBMCs.
Figures


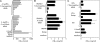
Comment in
-
Immune evasion: Gm18, a bacterial 'invisibility cloak'.Nat Rev Microbiol. 2012 Mar 5;10(4):238-9. doi: 10.1038/nrmicro2767. Nat Rev Microbiol. 2012. PMID: 22392494 No abstract available.
References
-
- Barrat F.J., Meeker T., Gregorio J., Chan J.H., Uematsu S., Akira S., Chang B., Duramad O., Coffman R.L. 2005. Nucleic acids of mammalian origin can act as endogenous ligands for Toll-like receptors and may promote systemic lupus erythematosus. J. Exp. Med. 202:1131–1139 10.1084/jem.20050914 - DOI - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases

