Oxygen Kinetics and Heart Rate Response during Early Recovery from Exercise in Patients with Heart Failure
- PMID: 22312564
- PMCID: PMC3270536
- DOI: 10.1155/2012/512857
Oxygen Kinetics and Heart Rate Response during Early Recovery from Exercise in Patients with Heart Failure
Abstract
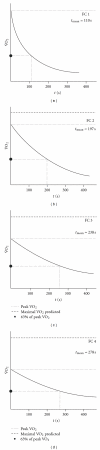
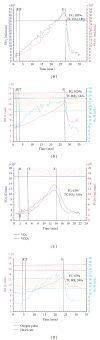
Background. The purpose of this study was to assess the post-exercise O(2) uptake and heart rate response in patients with heart failure (HF) in comparison to healthy individuals. Methods and Results. Exercise testing of all subjects was conducted according to the RITE-protocol. The study subjects were classified according to their peak oxygen uptake (peak VO(2)) in four groups: healthy individuals with a peak VO(2) >22 mL/kg/min (group 1, n: 50), and patients with HF and a peak VO(2) of 18-22 mL/kg/min, (group 2, n: 48), 14-18 mL/kg/min (group 3, n: 57), and <14 mL/kg/min (group 4, n: 31). Both peak VO(2) and HR declined more slowly in the patients with HF than in the normal subjects. Recovery of VO(2) and HR followed monoexponential kinetics in the early post-recovery phase. This enabled the determination of a time constant for both HR and VO(2) (TC VO(2) and TC HR). From group 1 to 4 there was a prolongation of the time constant for VO(2) and HR: TC VO(2) (group 1: 110 ± 34, group 2: 197 ± 43, group 3: 238 ± 80, and group 4: 278 ± 50 sec), and TC HR (group 1: 148 ± 82, group 2: 290 ± 65, group 3: 320 ± 58, and group 4: 376 ± 55 sec). Conclusion. The rate of decline of VO(2) and HR in the early post-exercise phase is inversely related to the peak VO(2). The time constant for oxygen uptake (TC VO(2)) and heart rate (TC HR) might prove a useful parameter for more precise monitoring and grading of HF.
Figures
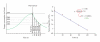
References
-
- Hansen JE, Sue DY, Oren A, Wasserman K. Relation of oxygen uptake to work rate in normal men and men with circulatory disorders. American Journal of Cardiology. 1987;59(6):669–674. - PubMed
-
- Wasserman K. Diagnosing cardiovascular and lung pathophysiology from exercise gas exchange. Chest. 1997;112(4):1091–1101. - PubMed
-
- Weber KT, Kinasewitz GT, Janicki JS, Fishman AP. Oxygen utilization and ventilation during exercise in patients with chronic cardiac failure. Circulation. 1982;65(6):1213–1223. - PubMed
-
- Gitt AK, Wasserman K, Kilkowski C, et al. Exercise anaerobic threshold and ventilatory efficiency identify heart failure patients for high risk of early death. Circulation. 2002;106(24):3079–3084. - PubMed
-
- Matsumura N, Nishijma H, Kojima S, Hashimoto F, Minami M, Yasuda H. Determination of anaerobic threshold for assessment of functional state in patients with chronic heart failure. Circulation. 1983;68(2):360–367. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous
