MAVIDOS Maternal Vitamin D Osteoporosis Study: study protocol for a randomized controlled trial. The MAVIDOS Study Group
- PMID: 22314083
- PMCID: PMC3395865
- DOI: 10.1186/1745-6215-13-13
MAVIDOS Maternal Vitamin D Osteoporosis Study: study protocol for a randomized controlled trial. The MAVIDOS Study Group
Abstract
MAVIDOS is a randomised, double-blind, placebo-controlled trial (ISRCTN82927713, registered 2008 Apr 11), funded by Arthritis Research UK, MRC, Bupa Foundation and NIHR.
Background: Osteoporosis is a major public health problem as a result of associated fragility fractures. Skeletal strength increases from birth to a peak in early adulthood. This peak predicts osteoporosis risk in later life. Vitamin D insufficiency in pregnancy is common (31% in a recent Southampton cohort) and predicts reduced bone mass in the offspring. In this study we aim to test whether offspring of mothers supplemented with vitamin D in pregnancy have higher bone mass at birth than those whose mothers were not supplemented.
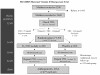
Methods/design: Women have their vitamin D status assessed after ultrasound scanning in the twelfth week of pregnancy at 3 trial centres (Southampton, Sheffield, Oxford). Women with circulating 25(OH)-vitamin D levels 25-100 nmol/l are randomised in a double-blind design to either oral vitamin D supplement (1000 IU cholecalciferol/day, n = 477) or placebo at 14 weeks (n = 477). Questionnaire data include parity, sunlight exposure, dietary information, and cigarette and alcohol consumption. At 19 and 34 weeks maternal anthropometry is assessed and blood samples taken to measure 25(OH)-vitamin D, PTH and biochemistry. At delivery venous umbilical cord blood is collected, together with umbilical cord and placental tissue. The babies undergo DXA assessment of bone mass within the first 14 days after birth, with the primary outcome being whole body bone mineral content adjusted for gestational age and age. Children are then followed up with yearly assessment of health, diet, physical activity and anthropometric measures, with repeat assessment of bone mass by DXA at age 4 years.
Discussion: As far as we are aware, this randomised trial is one of the first ever tests of the early life origins hypothesis in human participants and has the potential to inform public health policy regarding vitamin D supplementation in pregnancy. It will also provide a valuable resource in which to study the influence of maternal vitamin D status on other childhood outcomes such as glucose tolerance, blood pressure, cardiovascular function, IQ and immunology.
Figures
References
-
- Consensus development conference: diagnosis, prophylaxis, and treatment of osteoporosis. Am J Med. 1993;94:646–650. - PubMed
-
- Harvey N, Cooper C. In: Public Health Nutrition. Gibney M, Margetts B, Kearney J, Arab L, editor. Oxford: Blackwell Publishing; 2004. Disease prevention: Osteoporosis and hip fracture; pp. 357–369.
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Associated data
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Research Materials
Miscellaneous