Reduced Chrna7 expression in mice is associated with decreases in hippocampal markers of inhibitory function: implications for neuropsychiatric diseases
- PMID: 22314319
- PMCID: PMC3360578
- DOI: 10.1016/j.neuroscience.2012.01.033
Reduced Chrna7 expression in mice is associated with decreases in hippocampal markers of inhibitory function: implications for neuropsychiatric diseases
Abstract
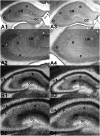
The α7* nicotinic acetylcholine receptor encoded by CHRNA7 (human)/Chrna7 (mice) regulates the release of both the inhibitory neurotransmitter GABA and the excitatory neurotransmitter glutamate in the hippocampal formation. A heterozygous (Het) deletion at 15q13.3 containing CHRNA7 is associated with increased risk for schizophrenia, autism, and epilepsy. Each of these diseases are characterized by abnormalities in excitatory and inhibitory hippocampal circuit function. Reduced Chrna7 expression results in decreased hippocampal α7* receptor density, abnormal hippocampal auditory sensory processing, and increased hippocampal CA3 pyramidal neuron activity in C3H mice Het for a null mutation in Chrna7. These abnormalities demonstrate that decreased Chrna7 expression alters hippocampal inhibitory circuit function. The current study examined the specific impact of reduced Chrna7 expression on hippocampal inhibitory circuits by measuring the levels of GABA, GABA(A) receptors, the GABA synthetic enzyme l-glutamic acid decarboxylase-65 (GAD-65), and the vesicular GABA transporter 1 (GAT-1) in wild-type (Chrna7 +/+) and Het (Chrna7 +/-) C3H α7 mice of both genders. GAD-65 levels were significantly decreased in male and female Het C3H α7 mice, whereas GABA(A) receptors were significantly reduced only in male Het C3H α7 mice. No changes in GABA and GAT-1 levels were detected. These data suggest that reduced CHRNA7 expression may contribute to the abnormalities in hippocampal inhibitory circuits observed in schizophrenia, autism, and/or epilepsy.
Published by Elsevier Ltd.
Figures

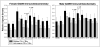

References
-
- Adams CE, Broide RS, Chen Y, Winzer-Serhan UH, Henderson TA, Leslie FM, Freedman R. Development of the alpha7 nicotinic cholinergic receptor in rat hippocampal formation. Brain Res Dev Brain Res. 2002;139:175–187. - PubMed
-
- Adams CE, Stevens KE. Evidence for a role of nicotinic acetylcholine receptors in schizophrenia. Front Biosci. 2007;12:4755–4772. - PubMed
-
- Ancin I, Barabash A, Vazquez-Alvarez B, Santos JL, Sanchez-Morla E, Martinez JL, Aparicio A, Pelaez JC, Diaz JA. Evidence for association of the non-duplicated region of CHRNA7 gene with bipolar disorder but not with Schizophrenia. Psychiatr Genet. 2010;20:289–297. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Miscellaneous

