Acquisition of EMT phenotype in the gefitinib-resistant cells of a head and neck squamous cell carcinoma cell line through Akt/GSK-3β/snail signalling pathway
- PMID: 22315058
- PMCID: PMC3304404
- DOI: 10.1038/bjc.2012.24
Acquisition of EMT phenotype in the gefitinib-resistant cells of a head and neck squamous cell carcinoma cell line through Akt/GSK-3β/snail signalling pathway
Abstract
Background: Epithelial mesenchymal transition (EMT) is known to be associated with chemoresistance as well as increased invasion/metastasis. However, the relationship between EMT and resistance to an epidermal growth factor receptor (EGFR) -targeting drug in head and neck squamous cell carcinoma (HNSCC) remains unknown. In this study, we investigated the acquisition of EMT by gefitinib in HNSCC cell line (UMSCC81B).
Methods: We isolated fibroblastoid variant (81B-Fb) from gefitinib-resistant UMSCC81B-GR3 cells obtained after increasing the doses of gefitinib treatment in vitro and examined EMT and its underlying mechanism.
Result: 81B-Fb cells exhibited fibroblast-like morphology, increased motility, loss of E-cadherin, acquisition of vimentin and snail expression. In 81B-Fb cells, downregulation of EGFR, which is mediated by increased ubiquitination, and activation of downstream protein kinase B (Akt), glycogen synthase kinase-beta (GSK-3β) signalling and upregulation of snail expression were observed compared with UMSCC81B cells. LY294002, but not U0126, suppressed foetal bovine serum or heregulin-β1-induced phosphorylation of Akt/GSK-3β and snail expression together with the inhibition of 81B-Fb cell motility. Furthermore, forced expression of EGFR resulted in partial restoration of gefitinib sensitivity and reversal of EMT.
Conclusion: These results suggest that EMT in the gefitinib-resistant cells is mediated by the downregulation of EGFR and compensatory activation of Akt/GSK-3β/snail pathway.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures
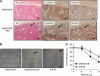
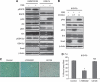
 ) and 81B-Fb cells (
) and 81B-Fb cells ( ). Bars= s.d., *P<0.05.
). Bars= s.d., *P<0.05.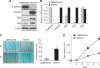
 ) and 81B-Fb cells (
) and 81B-Fb cells ( ). Loss of E-cadherin and acquisition of vimentin and snail expression are apparent. (C) Motility of UMSCC81B cells (
). Loss of E-cadherin and acquisition of vimentin and snail expression are apparent. (C) Motility of UMSCC81B cells ( ) and 81B-Fb cells (
) and 81B-Fb cells ( ) as measured by wound-closure assay. (D) In vitro growth rate of UMSCC81B cells (
) as measured by wound-closure assay. (D) In vitro growth rate of UMSCC81B cells ( ) and 81B-Fb cells (
) and 81B-Fb cells ( ). Bars=s.d., *P<0.05.
). Bars=s.d., *P<0.05.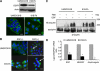
 ) and 81B-Fb cells (
) and 81B-Fb cells ( ). Bars=s.d., *P<0.05.
). Bars=s.d., *P<0.05.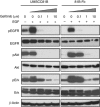
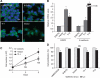
 ) and vector control (
) and vector control ( ). (D) Comparison of gefitinib sensitivity among various tumour cells with (
). (D) Comparison of gefitinib sensitivity among various tumour cells with ( ) and without gefitinib (
) and without gefitinib ( ). Bars=s.d., *P<0.05. Abbreviation: NS=not significant.
). Bars=s.d., *P<0.05. Abbreviation: NS=not significant.Similar articles
-
Snail regulated by PKC/GSK-3β pathway is crucial for EGF-induced epithelial-mesenchymal transition (EMT) of cancer cells.Cell Tissue Res. 2014 Nov;358(2):491-502. doi: 10.1007/s00441-014-1953-2. Epub 2014 Aug 16. Cell Tissue Res. 2014. PMID: 25124796
-
Epithelial mesenchymal transition is required for acquisition of anoikis resistance and metastatic potential in adenoid cystic carcinoma.PLoS One. 2012;7(12):e51549. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0051549. Epub 2012 Dec 14. PLoS One. 2012. Retraction in: PLoS One. 2014 Sep 10;9(9):e108117. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0108117. PMID: 23272116 Free PMC article. Retracted.
-
Epithelial-mesenchymal transition (EMT) induced by TNF-α requires AKT/GSK-3β-mediated stabilization of snail in colorectal cancer.PLoS One. 2013;8(2):e56664. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0056664. Epub 2013 Feb 19. PLoS One. 2013. PMID: 23431386 Free PMC article.
-
Epithelial to mesenchymal transition in head and neck squamous cell carcinoma.Oral Oncol. 2013 Apr;49(4):287-92. doi: 10.1016/j.oraloncology.2012.10.009. Epub 2012 Nov 19. Oral Oncol. 2013. PMID: 23182398 Free PMC article. Review.
-
The role of Snail in prostate cancer.Cell Adh Migr. 2012 Sep-Oct;6(5):433-41. doi: 10.4161/cam.21687. Epub 2012 Sep 1. Cell Adh Migr. 2012. PMID: 23076049 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Expression Analysis of GRHL3 and PHLDA3 in Head and Neck Squamous Cell Carcinoma.Cancer Manag Res. 2020 Jun 2;12:4085-4096. doi: 10.2147/CMAR.S252962. eCollection 2020. Cancer Manag Res. 2020. PMID: 32581582 Free PMC article.
-
The role of the dysfunctional akt-related pathway in cancer: establishment and maintenance of a malignant cell phenotype, resistance to therapy, and future strategies for drug development.Scientifica (Cairo). 2013;2013:317186. doi: 10.1155/2013/317186. Epub 2013 Dec 5. Scientifica (Cairo). 2013. PMID: 24381788 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Acquisition of EGFR TKI resistance and EMT phenotype is linked with activation of IGF1R/NF-κB pathway in EGFR-mutant NSCLC.Oncotarget. 2017 Sep 21;8(54):92240-92253. doi: 10.18632/oncotarget.21170. eCollection 2017 Nov 3. Oncotarget. 2017. PMID: 29190911 Free PMC article.
-
MicroRNA-200c increases radiosensitivity of human cancer cells with activated EGFR-associated signaling.Oncotarget. 2017 Jul 3;8(39):65457-65468. doi: 10.18632/oncotarget.18924. eCollection 2017 Sep 12. Oncotarget. 2017. PMID: 29029445 Free PMC article.
-
TRIM47 promotes hypopharyngeal and laryngeal cancers progression through promoting K63-linked ubiquitination of vimentin.Cancer Sci. 2025 Feb;116(2):367-380. doi: 10.1111/cas.16397. Epub 2024 Nov 25. Cancer Sci. 2025. PMID: 39584529 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Assinder SJ, Dong Q, Kovacevic Z, Richardson DR (2009) The TGF-beta, PI3K/Akt and PTEN pathways: established and proposed biochemical integration in prostate cancer. Biochem J 417: 411–421 - PubMed
-
- Cappuzzo F, Janne PA, Skokan M, Finocchiaro G, Rossi E, Ligorio C, Zucali PA, Terracciano L, Toschi L, Roncalli M, Destro A, Incarbone M, Alloisio M, Santoro A, Varella-Garcia M (2009) MET increased gene copy number and primary resistance to gefitinib therapy in non-small-cell lung cancer patients. Ann Oncol 20: 298–304 - PMC - PubMed
-
- Carraway III KL, Weber JL, Unger MJ, Ledesma J, Yu N, Gassmann M, Lai C (1997) Neuregulin-2 a new ligand of ErbB3/ErbB4-receptor tyrosine kinases. Nature 387: 512–516 - PubMed
-
- Chen HJ, Mok TS, Chen ZH, Guo AL, Zhang XC, Su J, Wu YL (2009) Clinicopathologic and molecular features of epidermal growth factor receptor T790M mutation and c-MET amplification in tyrosine kinase inhibitor-resistant Chinese non-small cell lung cancer. Pathol Oncol Res 15: 651–658 - PubMed
-
- Erjala K, Sundvall M, Junttila TT, Zhang N, , Savisalo M, , Mali P, Kulmala J, Pulkkinen J, Grenman R, Elenius K (2006) Signaling via ErbB2 and ErbB3 associates with resistance and epidermal growth factor receptor (EGFR) amplification with sensitivity to EGFR inhibitor gefitinib in head and neck squamous cell carcinoma cells. Clin Cancer Res 12: 4103–4111 - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

