Mechanism and distribution of glmS ribozymes
- PMID: 22315066
- PMCID: PMC5315370
- DOI: 10.1007/978-1-61779-545-9_8
Mechanism and distribution of glmS ribozymes
Abstract
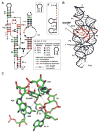
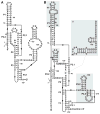
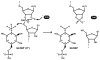
Among the nine classes of ribozymes that have been experimentally validated to date is the metabolite-responsive self-cleaving ribozyme called glmS. This RNA is almost exclusively located in the 5'-untranslated region of bacterial mRNAs that code for the production of GlmS proteins, which catalyze the synthesis of the aminosugar glucosamine-6-phosphate (GlcN6P). Each glmS ribozyme forms a conserved catalytic core that selectively binds GlcN6P and uses this metabolite as a cofactor to promote ribozyme self-cleavage. Metabolite-induced self-cleavage results in down-regulation of glmS gene expression, and thus the ribozyme functions as a key riboswitch component to permit feedback regulation of GlcN6P levels. Representatives of glmS ribozymes also serve as excellent experimental models to elucidate how RNAs fold to recognize small molecule ligands and promote chemical transformations.
Figures
Similar articles
-
An expanded collection and refined consensus model of glmS ribozymes.RNA. 2011 Apr;17(4):728-36. doi: 10.1261/rna.2590811. Epub 2011 Mar 2. RNA. 2011. PMID: 21367971 Free PMC article.
-
Core requirements for glmS ribozyme self-cleavage reveal a putative pseudoknot structure.Nucleic Acids Res. 2006 Feb 7;34(3):968-75. doi: 10.1093/nar/gkj497. Print 2006. Nucleic Acids Res. 2006. PMID: 16464827 Free PMC article.
-
Trans-acting glmS catalytic riboswitch: locked and loaded.RNA. 2007 Apr;13(4):468-77. doi: 10.1261/rna.341807. Epub 2007 Feb 5. RNA. 2007. PMID: 17283212 Free PMC article.
-
The glmS ribozyme: use of a small molecule coenzyme by a gene-regulatory RNA.Q Rev Biophys. 2010 Nov;43(4):423-47. doi: 10.1017/S0033583510000144. Epub 2010 Sep 8. Q Rev Biophys. 2010. PMID: 20822574 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Catalytic strategies of self-cleaving ribozymes.Acc Chem Res. 2008 Aug;41(8):1027-35. doi: 10.1021/ar800050c. Epub 2008 Jul 25. Acc Chem Res. 2008. PMID: 18652494 Review.
Cited by
-
Integration of an Expression Platform in the SELEX Cycle to Select DNA Aptamer Binding to a Disease Biomarker.ACS Omega. 2022 Mar 17;7(12):10804-10811. doi: 10.1021/acsomega.2c00769. eCollection 2022 Mar 29. ACS Omega. 2022. PMID: 35382297 Free PMC article.
-
EPR Distance Measurements on Long Non-coding RNAs Empowered by Genetic Alphabet Expansion Transcription.Angew Chem Int Ed Engl. 2020 May 11;59(20):7891-7896. doi: 10.1002/anie.201916447. Epub 2020 Mar 13. Angew Chem Int Ed Engl. 2020. PMID: 31981397 Free PMC article.
-
Self-cleavage of the glmS ribozyme core is controlled by a fragile folding element.Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2018 Nov 20;115(47):11976-11981. doi: 10.1073/pnas.1812122115. Epub 2018 Nov 5. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2018. PMID: 30397151 Free PMC article.
-
Riboswitches and Translation Control.Cold Spring Harb Perspect Biol. 2018 Nov 1;10(11):a032797. doi: 10.1101/cshperspect.a032797. Cold Spring Harb Perspect Biol. 2018. PMID: 29844057 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Phosphonate and Thiasugar Analogues of Glucosamine-6-phosphate: Activation of the glmS Riboswitch and Antibiotic Activity.ACS Chem Biol. 2023 Oct 20;18(10):2324-2334. doi: 10.1021/acschembio.3c00452. Epub 2023 Oct 4. ACS Chem Biol. 2023. PMID: 37793187 Free PMC article.
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

