Age-related impairment in insulin release: the essential role of β(2)-adrenergic receptor
- PMID: 22315324
- PMCID: PMC3282797
- DOI: 10.2337/db11-1027
Age-related impairment in insulin release: the essential role of β(2)-adrenergic receptor
Abstract
In this study, we investigated the significance of β(2)-adrenergic receptor (β(2)AR) in age-related impaired insulin secretion and glucose homeostasis. We characterized the metabolic phenotype of β(2)AR-null C57Bl/6N mice (β(2)AR(-/-)) by performing in vivo and ex vivo experiments. In vitro assays in cultured INS-1E β-cells were carried out in order to clarify the mechanism by which β(2)AR deficiency affects glucose metabolism. Adult β(2)AR(-/-) mice featured glucose intolerance, and pancreatic islets isolated from these animals displayed impaired glucose-induced insulin release, accompanied by reduced expression of peroxisome proliferator-activated receptor (PPAR)γ, pancreatic duodenal homeobox-1 (PDX-1), and GLUT2. Adenovirus-mediated gene transfer of human β(2)AR rescued these defects. Consistent effects were evoked in vitro both upon β(2)AR knockdown and pharmacologic treatment. Interestingly, with aging, wild-type (β(2)AR(+/+)) littermates developed impaired insulin secretion and glucose tolerance. Moreover, islets from 20-month-old β(2)AR(+/+) mice exhibited reduced density of β(2)AR compared with those from younger animals, paralleled by decreased levels of PPARγ, PDX-1, and GLUT2. Overexpression of β(2)AR in aged mice rescued glucose intolerance and insulin release both in vivo and ex vivo, restoring PPARγ/PDX-1/GLUT2 levels. Our data indicate that reduced β(2)AR expression contributes to the age-related decline of glucose tolerance in mice.
Figures
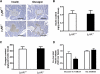
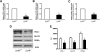
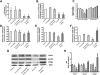
 , control, i.e. untreated INS-1E β-cells;
, control, i.e. untreated INS-1E β-cells;  , sh-scramble;
, sh-scramble;  , sh-scramble+empty vector;
, sh-scramble+empty vector;  , sh-β2AR;
, sh-β2AR;  , sh-β2AR+PPARγ; *P < 0.05 vs. control, Bonferroni post hoc test; basal is glucose 2.8 mmol/L. Equal amount of proteins from three independent experiments was analyzed by Western blotting and quantified by densitometry (G and H ). *P < 0.05 vs. sh-scramble. AU, arbitrary units. (See also
, sh-β2AR+PPARγ; *P < 0.05 vs. control, Bonferroni post hoc test; basal is glucose 2.8 mmol/L. Equal amount of proteins from three independent experiments was analyzed by Western blotting and quantified by densitometry (G and H ). *P < 0.05 vs. sh-scramble. AU, arbitrary units. (See also 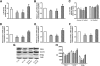
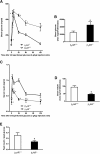
 , age 6 months (mos);
, age 6 months (mos);  , 20 months;
, 20 months;  , 20 months AdEmpty;
, 20 months AdEmpty;  , 20 months Adβ2AR. *P < 0.05 vs. β2AR+/+ 6 months, Bonferroni post hoc test.
, 20 months Adβ2AR. *P < 0.05 vs. β2AR+/+ 6 months, Bonferroni post hoc test.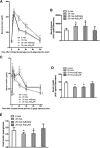
References
-
- Basu R, Breda E, Oberg AL, et al. Mechanisms of the age-associated deterioration in glucose tolerance: contribution of alterations in insulin secretion, action, and clearance. Diabetes 2003;52:1738–1748 - PubMed
-
- Gumbiner B, Polonsky KS, Beltz WF, Wallace P, Brechtel G, Fink RI. Effects of aging on insulin secretion. Diabetes 1989;38:1549–1556 - PubMed
-
- Reaven E, Wright D, Mondon CE, Solomon R, Ho H, Reaven GM. Effect of age and diet on insulin secretion and insulin action in the rat. Diabetes 1983;32:175–180 - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials

