Remarkable transglycosylation activity of glycosynthase mutants of endo-D, an endo-β-N-acetylglucosaminidase from Streptococcus pneumoniae
- PMID: 22318728
- PMCID: PMC3322811
- DOI: 10.1074/jbc.M112.340497
Remarkable transglycosylation activity of glycosynthase mutants of endo-D, an endo-β-N-acetylglucosaminidase from Streptococcus pneumoniae
Erratum in
- J Biol Chem. 2012 Jun 1;287(23):19339
Abstract
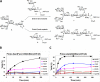
Endo-β-N-acetylglucosaminidase from Streptococcus pneumoniae (Endo-D) is an endoglycosidase capable of hydrolyzing the Fc N-glycan of intact IgG antibodies after sequential removal of the sialic acid, galactose, and internal GlcNAc residues in the N-glycan. Endo-D also possesses transglycosylation activity with sugar oxazoline as the donor substrate, but the transglycosylation yield is low due to enzymatic hydrolysis of the donor substrate and the product. We report here our study on the hydrolytic and transglycosylation activity of recombinant Endo-D and its selected mutants. We found that Endo-D preferred core-fucosylated N-glycan for hydrolysis but favored nonfucosylated GlcNAc acceptor for transglycosylation. Several mutants showed significantly enhanced transglycosylation efficiency over the wild type enzyme. Two mutants (N322Q and N322A) were identified as typical glycosynthases that demonstrated remarkable transglycosylation activity with only marginal or no product hydrolysis activity. Kinetic studies revealed that the N322Q [corrected]and N322A glycosynthases had much higher catalytic efficiency for glycosylating the nonfucosylated GlcNAc acceptor. In comparison, the N322Q was much more efficient than N322A for transglycosylation. However, N322Q and N322A [corrected] could not take more complex N-glycan oxazoline as substrate for transglycosylation, indicating their strict substrate specificity. The usefulness of the N322Q glycosynthase was exemplified by its application for efficient glycosylation remodeling of IgG-Fc domain.
Figures
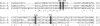



References
-
- Robbins P. W., Trimble R. B., Wirth D. F., Hering C., Maley F., Maley G. F., Das R., Gibson B. W., Royal N., Biemann K. (1984) Primary structure of the Streptomyces enzyme endo-β-N-acetylglucosaminidase H. J. Biol. Chem. 259, 7577–7583 - PubMed
-
- Tarentino A. L., Quinones G., Schrader W. P., Changchien L. M., Plummer T. H., Jr. (1992) Multiple endoglycosidase (Endo) F activities expressed by Flavobacterium meningosepticum. Endo F1: molecular cloning, primary sequence, and structural relationship to Endo H. J. Biol. Chem. 267, 3868–3872 - PubMed
-
- Tarentino A. L., Quinones G., Changchien L. M., Plummer T. H., Jr. (1993) Multiple endoglycosidase F activities expressed by Flavobacterium meningosepticum endoglycosidases F2 and F3: molecular cloning, primary sequence, and enzyme expression. J. Biol. Chem. 268, 9702–9708 - PubMed
-
- Kadowaki S., Yamamoto K., Fujisaki M., Tochikura T. (1991) Microbial endo-β-N-acetylglucosaminidases acting on complex-type sugar chains of glycoproteins. J. Biochem. 110, 17–21 - PubMed
-
- Yamamoto K., Kadowaki S., Fujisaki M., Kumagai H., Tochikura T. (1994) Novel specificities of Mucor hiemalis endo-β-N-acetylglucosaminidase acting complex asparagine-linked oligosaccharides. Biosci. Biotechnol. Biochem. 58, 72–77 - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases

