A monitoring and advisory system for diabetes patient management using a rule-based method and KNN
- PMID: 22319334
- PMCID: PMC3274186
- DOI: 10.3390/s100403934
A monitoring and advisory system for diabetes patient management using a rule-based method and KNN
Abstract
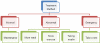
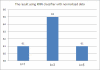
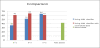
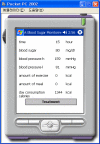
Diabetes is difficult to control and it is important to manage the diabetic's blood sugar level and prevent the associated complications by appropriate diabetic treatment. This paper proposes a system that can provide appropriate management for diabetes patients, according to their blood sugar level. The system is designed to send the information about the blood sugar levels, blood pressure, food consumption, exercise, etc., of diabetes patients, and manage the treatment by recommending and monitoring food consumption, physical activity, insulin dosage, etc., so that the patient can better manage their condition. The system is based on rules and the K Nearest Neighbor (KNN) classifier algorithm, to obtain the optimum treatment recommendation. Also, a monitoring system for diabetes patients is implemented using Web Services and Personal Digital Assistant (PDA) programming.
Keywords: KNN classifier algorithm; diabetes; monitoring system; ubiquitous healthcare.
Figures









References
-
- Jiang M., Fu P., Chen H.X., Chen M.S., Xing B., Sun Z.H., Deng P., Wang G., Xu Y., Wang Y. A Dynamic Blood Information Management System Based on RFID. Proceedings of the 2005 IEEE Engineering in Medicine and Biology; Shanghai, China. 2005. pp. 546–549. - PubMed
-
- Kun S.M. Aju University; Seoul, Korea: 2006. A Study of Local Government of U-healthcare Service. M.A. Thesis,
-
- U-health, Available online: www.komdj.com/upfiles/pdf_report/51.pdf (Access on 1 April 2010).
-
- Jang S., Lee M., Kim J. Ubiquitous Sensor Application Service and A tendency of Development. IT Soc. Mag. 2007:9–22.
-
- Group of KangNam Hospital Diabetes . Home Health care of Diabetes. WoongJin Knowledge House; Seoul, Korea: 2005.
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

