Usage and attitudes of physicians in Japan concerning traditional Japanese medicine (kampo medicine): a descriptive evaluation of a representative questionnaire-based survey
- PMID: 22319543
- PMCID: PMC3273038
- DOI: 10.1155/2012/139818
Usage and attitudes of physicians in Japan concerning traditional Japanese medicine (kampo medicine): a descriptive evaluation of a representative questionnaire-based survey
Abstract
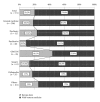
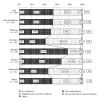
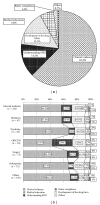
Kampo medicine has been the primary medical model in Japan until the mid 1800s, regained a prominent role in today's Japanese medical system. Today, 148 herbal Kampo formulas can be prescribed under the national health insurance system, allowing physicians to integrate Kampo in their daily practice. This article aims to provide information about the extent to which Kampo is now used in clinics throughout Japan and about physician's current attitudes toward Kampo. We used the results of a 2008 survey that was administered to physicians throughout Japan (n = 684). The data showed that 83.5% of physicians currently use Kampo in the clinic, although the distribution of physicians who use Kampo differ widely depending on the specialty and provided a breakdown of Kampo usage by specialty. It will be interesting to see how each specialty incorporates Kampo into its respective field as Kampo continues to play a pertinent role in Japanese medical system.
Figures



References
-
- Fujiwara K, Imanishi J, Watanabe S, Ozasa K, Sakurada K. Changes in attitudes of Japanese doctors toward complementary and alternative medicine—comparison of surveys in 1999 and 2005 in Kyoto. Evidence-Based Complementary and Alternative Medicine. 2011;2011:7 pages. Article ID 608921. - PMC - PubMed
-
- Yamashita H, Tsukayama H, Sugishita C. Popularity of complementary and alternative medicine in Japan: a telephone survey. Complementary Therapies in Medicine. 2002;10(2):84–93. - PubMed
-
- Watanabe S, Imanishi J, Satoh M, Ozasa K. Unique place of Kampo (Japanese traditional medicine) in complementary and alternative medicine: a survey of doctors belonging to the regional medical association in Japan. Tohoku Journal of Experimental Medicine. 2001;194(1):55–63. - PubMed
-
- Imanishi J, Watanabe S, Satoh M, Ozasa K. Japanese doctors’ attitudes to complementary medicine. The Lancet. 1999;354(9191):1735–1736. - PubMed
-
- Yagi M, Homma S, Kubota M, et al. The herbal medicine Rikkunshi-to stimulates and coordinates the gastric myoelectric activity in post-operative dyspeptic children after gastrointestinal surgery. Pediatric Surgery International. 2004;19(12):760–765. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

