The location of maxillary sinus ostium and its clinical application
- PMID: 22319687
- PMCID: PMC3266099
- DOI: 10.1007/s12070-010-0047-z
The location of maxillary sinus ostium and its clinical application
Abstract
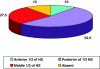
The endoscopic sinus surgeons must have a detailed knowledge of inconsistent location of maxillary sinus openings in any interventional maxillary sinus surgeries as it relates to the orbital floor, ethmoid infundibulum and the nasolacrimal duct. Forty cadaver head and neck specimens had been cut sagittally through the nose, such that the lateral nasal wall had been preserved. The findings were documented with an emphasis on location of the maxillary sinus openings. In the present study maxillary sinus ostium opened more commonly into posterior third of the hiatus semilunaris. Accessory maxillary ostium was another variation seen in nearly three-fourths of the cases which opened into membranous meatus inferior to the uncinate process.
Keywords: Accessory maxillary ostium; Maxillary os; Maxillary sinus; Ostiomeatal unit.
Figures


References
-
- Kumar H, Choudhry R, Kakar S. Accessory maxillary ostia : topography and clinical application. J Anat Soc India. 2001;50(1):3–5.
-
- Hollinshed WH, Rosse C. Text book of Anatomy. 4. Philadelphia: Herper and Row; 1985. pp. 976–985.
-
- Anon JB, Rontal M, Zinreich SJ. Anatomy of the paranasal sinuses. New York: Thieme Medical Publishers; 1996. pp. 3–41.
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
