Peripheral auditory assessment in minor head injury: a prospective study in tertiary hospital
- PMID: 22319716
- PMCID: PMC3109972
- DOI: 10.1007/s12070-011-0117-x
Peripheral auditory assessment in minor head injury: a prospective study in tertiary hospital
Abstract
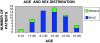
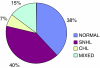
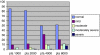
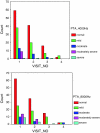
Hearing loss is a common problem encountered in ENT practice. Hearing loss following head injury is a major medical problem in both adults and children, which may go unnoticed when it does not affect speech frequencies. Sensorineural hearing loss at high frequencies is a common finding in minor head injury. Patients with history suggestive of mild head injury (MHI) according to Glasgow coma scale score were evaluated. The most common cause of MHI was road traffic accidents involving two wheeler riders without helmets. Higher the frequencies affected, and severe the hearing loss, poorer was the prognosis. Distortion product oto-acoustic emissions assessment at 3000 and 4000 Hz were found to be significant and has a higher predictive value in assessing outer hair cell damage.
Keywords: DPOAE; Hearing loss; Minor head injury; Road traffic accidents.
Figures
References
-
- The Times of India 14 July 2008
-
- Alexander MP. Mild traumatic brain injury. Neurology. 1995;45:1253–1260. - PubMed
-
- Mishra BK, Banerji AK, Mohan D. Two-wheeler injuries in Delhi, India: a study of crash victims hospitalized in a neuro-surgery ward. Accid Anal Prev. 1984;16(5–6):407–416. doi: 10.1016/0001-4575(84)90053-8. - DOI
-
- Gururaj G (2000) Epidemiology of road traffic injuries in Bangalore. In: Proceedings of the 5th world conference on injury prevention and control. Macmillan, New Delhi
-
- Schuknecht HF. Mechanism of inner ear injury from blows to the head. Ann Otol Rhinol Laryngol. 1969;78:253–262. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous